Football is one of the most popular sports in the world, both for cheering and playing. With teamwork that requires both planning and personal talent, football offers awe and challenge that meet current rapid play on the field. Players tend to collide into each other on the field and injuries can occur at any time, especially towards the end of play when fatigue sets in. The most common football injury is muscle injury, but other serious injuries include torn ligament, broken ankle, or concussion, which will require long term care. Thus, it is important to prepare yourself before entering the field to prevent injury and immediately receive treatment if injured.
Cause of Football Injury
- Inadequate physical conditioning
If the players are not physically ready in their fitness and connective tissues, or imbalanced homeostasis, it may lead to injuries during practice or competition. - Not enough stretching before and after football session
Warming up and cooling down before and after playing sports will help condition the muscles and tendons to have more flexibility and ready for competition and rehabilitation. FIFA 11+ warm up program which has been well designed can reduce injuries by up to 30%. - Inadequate or lack of protective gears
When choosing football shoes, for example, suitability should be kept in mind. If improper shoes are used, such as using sneakers on grass, it may cause a slip and injury to the player. Currently, football fields with imitation grass is popular in Thailand. These synthetic grasses have more friction than real grass. If the player chooses studs or blades, there might be too much friction leading to serious injuries. Same thing with protective gears, such as shin guards, which can reduce force during contact and reduce serious injuries. - Excessive physical exertion
During practice or competition, players will need to run at high speed, jump and put force on their legs all the time. If the players did not assess their physical condition, it may lead to injuries from overusage, such as ligament inflammation in the groin, hip, knee and ankle, or serious injuries such as stress fractures. - Inadequate understanding of game rules
Football rules have evolved over time to increase safety during play. For example, use of elbow, sliding from behind, or raising foot too high are no longer allowed. If players do not keep up with current rules, it may cause injuries to them or their opponents. - Unexpected accidents
Since football is a contact sport that requires agility and strength, accidents can happen any time leading to concussion, broken bones, or acute heart failure.
Football – related Injuries
Playing football can lead to injuries at multiple locations, most commonly in the thighs, knees, ankles or groin, respectively.
1) Thigh Muscle Injury
The hamstrings, quadriceps, and adductors can become inflamed or torn, which are the most common football injuries. This is because players need to use these muscles to run, jump, and kick incessantly. We can see in images of footballers running at their top speed and all of the sudden, they can no longer continue due to injuries. Recovery period depends on the severity of the injury. It may take only a few days for minor injuries or a few months for more severe injuries. Reinjury is also common among this group of muscles.
2) Ankle Sprain
Ankle sprain usually occurs as a result of players colliding into each other, causing the ankle to overturn. Mostly, the ankles will be turned inward causing injuries to the muscles on the outside. Minor injuries can lead to swells and pain around the injured ligaments. The player may be able to put some weight on the ankle. If they ligament is torn, most will suffer from severe pain, swelling from inflammation and internal bleeding, and they will not be able to put weight on the ankle. In the case of extreme injury or all ankle ligaments are torn, the ankle will lose stability, swell from inflammation and internal bleeding. They will not be able to put weight on the affected ankle. If they do not receive proper treatment, it can lead to chronic ankle instability and subsequent surgery.
3) Anterior Cruciate Ligament – ACL Tear
Although this is not the most common injury, ACL tear can cause severe injury and can be seen through haunting images of players on the field. They will not be able to continue playing because they cannot put weight on the affected ankle and they will require surgery. Recovery can take more than 6 months. An injury that causes distorted ankle often is accompanied by a loud “pop” in the ankle. The knee may be inflamed as well. It is discovered that most of the time, this is a non-contact injury. Players can exercise and strengthen their ACL to reduce the risk of injury. Furthermore, Today’s technology allows for minimal invasive surgery to repair the tear so that players can still play with full efficient post-surgery.
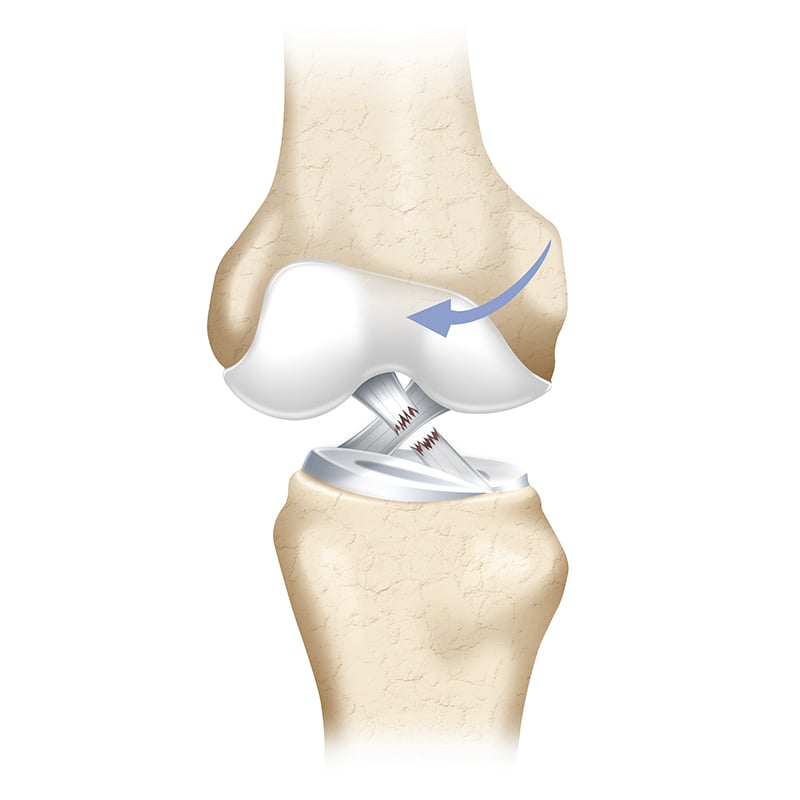
4) Meniscus & Chondral Injury
Other than ACL injury, impact or distortion of the knees can lead to meniscus and chondral injuries as well. Footballers may experience knee swelling after a game, the knee joint may lock so that it cannot be stretched or bent, occasional swollen knee. If players feel that they cannot stretch out the knee after injury, please contact an orthopedist immediately to find the root cause. If the injury is severe such as lock bucket handle meniscus tear, minimal invasive surgery is necessary to repair the meniscus rapidly to prevent premature knee osteoarthritis.
5) Knee Ligament Injury
The knee is the most common injury in football, where the ligaments around the knee can be injured. For example, medial collateral ligament, or MCL, can be injured due to impact or pumping the ball. The knee can twist inward causing it to swell and making it painful to stretch or bend the knee. Particularly, if the injury is severe, the patient may not be able to put any weight on that knee. Treatment duration depends on the severity of the injury. If the ligament is torn, it may take up to 6 – 8 weeks to recover. Alternatively, the patella tendon can be injured from repetitive actions without any apparent trauma. The pain may irradiate along the patella tendon, in the patella, or down the tibia. Physical therapy will be necessary, while practice and matches will need to be adjusted accordingly.
6) Bone Fracture
Physical contact during a football match can cause bone fractures, such as the tibia, ankle or the clavicle bone, all of which are considered serious injuries. The patient should try to move as little as possible and should go to the hospital immediately. If there is a tear as well, the patient should receive surgery as soon as possible. In playing football, bone fractures should be treated by surgery to put the bones in the correct position and rehabilitate surrounding joints and muscles as soon as possible to prevent complications from wearing a cast. These complications include joint attachment and muscle atrophy. Other than contact injury, bone fractures can be caused by stress fracture due to overuse, mostly around the 5th metatarsal bone in the foot. It is particularly correlative to football players who have high arches than usual.
7) Head Concussion
If contact occurs in the head or neck area, the player can lose consciousness, suffer seizure, or severe headache with blurred vision, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, numbness in the legs and arms, pain in the neck, or confusion. There are signs of brain injury or brain trauma. The player needs to rest from practice or competition and seek medical attention immediately. A head concussion may show signs as time goes by. If there is any sign, the player should stop and observe for further signs. They should only return to the field after a consultation with the doctor. If they return to play too early, it may be more harmful to the player and the team.
8) Sudden Cardiac Arrest
Sudden cardiac arrest or heart failure is an emergency in football. Although the chance is low, it can occur to any one of any sex and age, regardless of whether they are professional athletes or not. If a player falls and seems like they lost consciousness without any physical contact, everyone should think of sudden cardiac arrest. Medics will start live-saving CPR and use and AED immediately. If the player is older than 35 years old, it is usually due to atherosclerosis. If the player is younger than 35 years old, the cause may be from myocarditis, arrhythmia, or congenital heart condition. Currently, FIFA gives sudden cardiac arrest high priorities. Field medics have been regularly trained to treat the condition in every match. It is recommended that players should receive physical exam, EKG, and echocardiograph regularly to screen for any abnormal conditions prior to a match for their own safety.
9) Athletic Pubalgia
Football players tend to suffer from groin injuries. There might be dull pain in the pubis or groin area. There might be a mass as well. If the player suffers from chronic injury, they should consult sports medicine specialist to find the root cause. It may be due to a hernia, pubic symphysis, hip, or adductor and iliopsoas injuries. Treatment varies depending on the location and cause of the pain. Surgery may be necessary if it is a hernia.
Treatment for Football Injuries
When football-related injuries occur, first aid is integral to treatment. Football injuries may be treated by using PRICE:
- P – Protect: Protect from further injuries, such as use a splinter on the injured area or use a cane to help the player walk.
- R – Rest: Rest from playing and movement so that the injury can heal. Observe for 2 – 3 days.
- I – Ice: Put ice on the affected area about 15 – 20 minutes each time and as often as necessary.
- C – Compression: Use a wrap around the affected area to reduce swelling and movement
- E – Elevate: Keep the affected area above the heart to reduce swelling, such as raise the legs higher than the heart.
Furthermore, please consult sports medicine specialist to diagnose and treat the injury accordingly, such as medication, physical therapy, equipment to reduce pain, rehabilitate tendons and muscles. If severe, surgery may be necessary. BASEM aims to treat using targeted therapy to reduce injury around the joints with advanced minimally invasive surgery to reduce complications and enhance recovery by a team of sports medicine specialists who are experienced in treating professional athletes and national athletes so they can return to high level of competition. Together with specialists from multidisciplinary sports medicine and individualized rehabilitation program after surgery as well as keeping the body fit during rehabilitation. Test for readiness after treatment will be administered to ensure physical fitness and protection against future injuries. The medical team will help the player start to exercise or return to competition in full health again.
Preventing Football-Related Injuries
Prevention of football-related injuries can be done by:
- Physical preparedness. Before going on the field for training, players should balance between endurance and muscle strength training. Warm up every time before going on the field and stretch after practice. Drink plenty of water to reduce dehydration. Rest at least 8 hours a day. Eat complete meals, especially carbohydrates, which are the main source of energy during play.
- Wear protective gear. Use shin guards to reduce impact on the legs and shin. Wear studs that have suitable blades for the field so that they will not slip during play. Use tapes to lock the ankles to prevent injuries, especially in players who have had ankle sprains or instability.
- Self-exam before game. Players should be in fit physical condition and injury-free. If they suffer from a previous injury, such as around the muscles, joints, and tendons, further injuries may exacerbate the condition leading to longer treatment time. If the joints are unstable, they must heal completely before players can return to the field to avoid severe injuries, such as torn ligaments. If players continue to force physical exertion, it may be harmful to the knee joints leading to premature knee osteoarthritis. Athletes should receive complete physical exam every time before a match to screen for and prevent injuries.
- Know the basics about football injuries. This will help players give themselves the right first aid. For example, contact injuries that cause bruising or abrasion from studs should be cleaned and compressed with ice.
If any player suffers from football injury, administer the right first aid, perform self-assessment, and consult sports medicine specialist to examine and rehabilitate as necessary so that they can play with confidence.
Football Performance Program
Bangkok Academy of Sports and Exercise Medicine (BASEM) at Bangkok Hospital or FIFA Medical Centre of Excellence offers treatment, surgery, rehabilitation, physical examination of athletes of all levels as per FIFA standards. Amateur athletes can boost their fitness and check their physical readiness with Football Performance Program, which is designed specifically for football players. Our team of sports medicine at BASEM are ready to offer consultation and exercise regimen to increase efficiency, prevent injuries, and exercise per FIFA 11+, which can reduce up to 30% of football-related injuries. Professional athletes can choose Fit for Performance Program, which follows FIFA Pre-competition Medical Assessment (FIFA PCMA) to cover physical assessment, bones and muscles check, blood work and chest X-ray, as well as cardiovascular exam by medical specialists to screen for risk and readiness before a match.










