Gallstones are one of the most common digestive diseases which small stones are formed in the gallbladder. If gallstones lodge in a bile duct and cause a blockage, it eventually results in severe life-threatening complications such as bile duct inflammation and infection, pancreatitis or cholecystitis (an inflammation of gallbladder). In addition, if left untreated, it might increase risk of “gallbladder cancer”. Statistical data reviews that gallstones have been commonly found in women rather than men, age between 30-50. Since signs and symptoms are quite similar, patients with gallstones often misunderstand that they might have “peptic ulcer”. Self-treatment by taking antacid and anti-ulcer medications without having an accurate diagnosis results in an increased severity, frequently presented with emergency conditions that require immediate treatments. Knowing the early signs of gallstones must be aware in order to get the disease diagnosed in due time and receive appropriate medical treatment.
Function of Gallbladder
Gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped, hollow structure located under the liver on the right side of the abdomen. The gallbladder stores and concentrate a digestive fluid called “bile” which is a yellowish-brown fluid used to break up and digest fatty foods in the small intestine.
Get to Know “Gallstones”
Gallstones (or cholelithiasis) are responsible for one of the most prevalent biliary disorders. Gallstones are hardened deposits of digestive fluid (bile) that can form in the gallbladder. The stones are mainly caused from the precipitation of either calcium salts or cholesterol in bile.The appearance of gallstones may vary depending on their types. Classification by compositions, there are 3 main types of gallstones:
Cholesterol gallstones:
The most common type of gallstone is called “cholesterol gallstones”, often appearing in chalk white or greenish-yellow due to undissolved cholesterol as the main component.
Pigment gallstones:
Pigment gallstones are dark brown or black stones containing bilirubin. Major causes might originate from the abnormalities of blood such as hemolytic anemia and liver diseases such as jaundice and cirrhosis.
Mixed gallstones:
Mixed gallstones are the mixture of both cholesterol and pigment gallstones with a sticky mud-like appearance. They typically arise secondary to the infection of the biliary tract, liver and pancreas.
Signs and Symptoms of Gallstones:
Gallstones range in size from as small as a grain of sand to the size of a golf ball. The size of stones may increase with time. There might be only a single stone or up to several hundreds of stones at the same time. The risk to develop gallbladder cancer is strongly associated with a larger size of gallstones.
Gallstones may cause no signs or symptoms. However, if a gallstone lodges in a duct and causes a blockage, the consequent signs and symptoms may include:
- Flatulence
- Bloating or having chronic digestive problems after consuming high-fat diets
- Severe and sudden pain in the upper right abdomen.
- Pain that radiates to right shoulder or back (between shoulder blades)
- Nausea and vomitting (mainly from cholecystitis or inflammation of gallbladder)
- High fever and chills
- Jaundice, dark urine or pale stool (if there is an obstruction in bile duct, affecting the draining of biliary system)
Risks Factors of Gallstones
- Being female age 40 or older
- Being the elderly over 60
- Obesity and overweight
- Hypercholesterolemia (high level of blood cholesterol)
- Diabetes
- Hematologic disorders such as anemia and thalassemia
- Being pregnant or having had several children
- Taking medications that contain estrogen such as oral contraceptives or hormone replacement therapy
- Losing weight very quickly or having fasting period (e.g. Ramadan)
- Taking some lipid lowering drugs (some side effects on bile composition and cholesterol gallstone formation)
- Having a family history of gallstones
Diagnosis of Gallstones
Combined with physical and full abdominal examinations, diagnosis of gallstones is typically confirmed by an upper abdominal ultrasound, a radiological imaging test which is performed by gastrointestinal specialists. By using the high-frequency sound waves to create the images of the inside of abdomen, the images created from ultrasound scan clearly reveal the detail of gallstones. However, MRI scan (magnetic resonance imaging) might be additionally recommended if some stones remain invisible. Gallstone complications may be further detected by blood tests.
Treatment of Gallstones
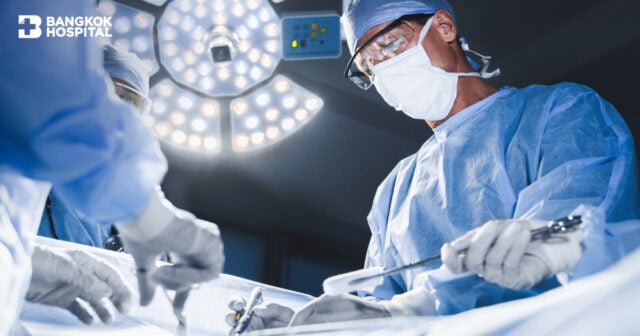
If the patient is an appropriate candidate for surgery, surgical removal of gallbladder is mostly advised to all cases in order to reduce disease severity and recurrence of stones which is very common. There are 2 types of gallbladder surgery:
- Open surgery (open cholecystectomy): a surgery to remove the gallbladder via a single, large open incision (5- to 7-inch) in the abdomen. Open surgery might be indicated if severe inflammation of bile duct or gallbladder is presented which might lead to the ruptures of gallbladder. Due to the size of incision, patients usually experience more pain and need a longer recovery time.
- Laparoscopic surgery (laparoscopic cholecystectomy or LC): a minimally invasive surgery to remove gallbladder which is performed through 4-5 small incisions (each one inch or less in length) instead of making an open large cut in the abdomen. The surgical instruments are inserted via these small incisions such as a laparoscope, a narrow tube with a camera. This allows surgeons to clearly visualize all dimensions of gallbladder on a screen before having it removed accurately and safely.
With laparoscopic cholecystectomy, smaller incisions cause less pain after surgery with fewer complications such as less blood loss and lower rates of post-operative infections. Cosmetic benefits gained from laparoscopic surgery is additionally superior to the open procedure. Furthermore, surgery to remove the gallbladder with a laparoscope does not require the muscles of abdomen to be cut whereas open surgery does. Patients thus have a faster recovery time and shorter of hospital stay resulting in a quick return to daily activities.
After gallbladder removal surgery, patients do not have to be concerned about their digestive functions since gallbladder only holds bile acid and it is not essential to healthy digestion. However, to enhance the digestive health and avoid abdominal bloating, the consumption of high fat diets must be controlled with the proper amount of vegetables, fruits and easy-to-digest foods such as fish.
“Gallstones … Watch Out! If you are a woman over 40+”
Amazingly, cholesterol gallstones have been commonly found in women above 40 mainly owning to elevated estrogen levels, resulting in increased hepatic secretion of biliary cholesterol and cholesterol supersaturated bile. Other risk factors include hypercholesterolemia (high level of blood cholesterol), taking medications that contain estrogen such as oral contraceptives or hormone replacement therapy, having had several children, being diabetic or being diagnosed with thalassemia.
Prevention of Gallstones
The most effective way to reduce risk of “gallstones” is to remain healthy including weight reduction if obese, avoiding the consumption of fatty diets with high calories, taking high-fiber containing foods such as vegetables and fruits. Hypercholesterolemia (high level of blood cholesterol) and diabetics must be strictly well controlled. More importantly, having a regular health checkup every year helps to early screen gallstones before its symptom arises. If any suspected signs and symptoms of gallstones are manifested, a full physical examination and upper abdominal ultrasound scan are immediately recommended.
If gallstones remain negligently untreated, it might lead to life-threatening conditions such as cholecystitis and sepsis. Moreover, it might potentially trigger the risk to develop “gallbladder cancer” in the future.