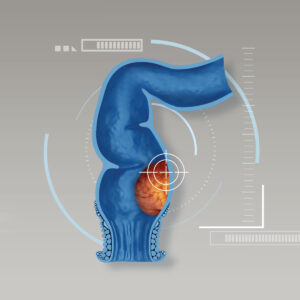
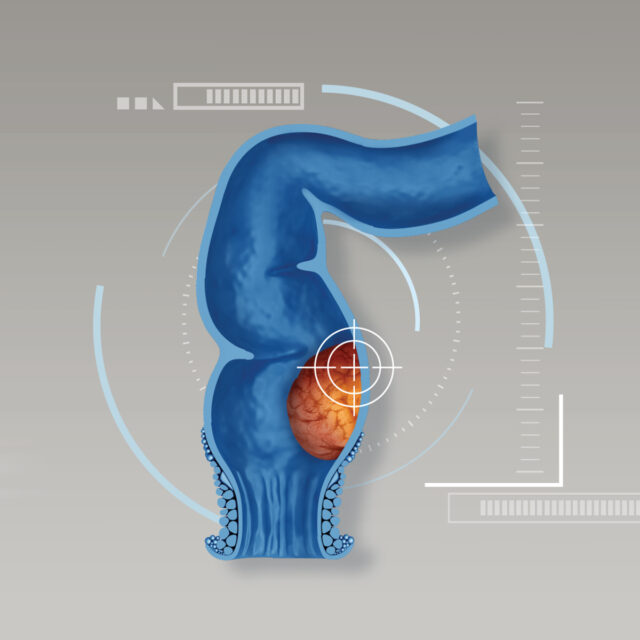
Gallbladder polyps are growths that protrude from the lining of the inside of the gallbladder. Although this condition might not be a common digestive disease, it is often accidentally diagnosed by abdominal ultrasound. Gallbladder polyps are mostly found in men, rather than women. Polyps can be cancerous, but they rarely are. About 70-80 percent of gallbladder polyps are benign. Annual check-ups remain crucially important. If gallbladder polyps are detected at the earlier stage, treatment can be successfully given.
Get to know “gallbladder polyps”
Gallbladder polyps are small, abnormal growths of tissue with a stalk protruding from the lining of the inside of the gallbladder. Gallbladder polyps typically do not cause any symptoms. They are usually found incidentally during performing abdominal ultrasound. The most common type is pseudopolyps, projecting masses of scar tissue typically caused by cholesterol deposits and inflammation. Psuedopolyps do not exhibit correlations with cancerous cells. True gallbladder polyps or neoplastic polyps are rarely found and can be single polyp or multiple polyps. However, they can be both benign and malignant cells. Importantly, gallbladder polyps do not produce any specific symptoms. Most cases have been discovered by abdominal ultrasound during annual health check-ups.
Treatment of gallbladder polyps
If gallbladder polyps are found without indications for surgery, close follow-up, every 6-12 months is highly advised. However, if the patients have certain indications to receive surgical treatment, immediate surgery should be performed.
Minimally invasive surgery to remove gallbladder
Compared to open surgery which open cut is required, minimally invasive surgery with laparoscopic technique helps enhancing surgical accuracy and promoting safety. During the procedure, small incisions are made instead of having a large open put required in open surgery. A small tube attached with a tiny camera (laparoscope) is inserted into one incision. Guided by this camera which internal images are displayed on the monitoring screen, the surgeon then inserts tiny surgical instruments through other incisions to safely remove gallbladder. Due to the advancements in laparoscopic instrument with 4K Ultra High Definition and Advanced 3D laparoscopic surgery, it enables surgeons to clearly visualize the surgical field in the abdominal cavity including internal organs, blood vessels and nerves. Advanced technology of laparoscopic camera with ultra high definition and resolution results in a better visualization of hidden areas that could not be previously seen. Smaller incisions cause less pain, less blood loss and reduced post-operative complications as well as a faster recovery time and a quicker return to normal activities. Nevertheless, minimally invasive surgery might not be suitable for highly complicated conditions. In such a case, open surgery might be preferably chosen. Severity, numbers of polyps and polyp invasive degree play a major role to determine appropriate surgical technique.
Indications for surgery to remove gallbladder polyps
- Polyps sized larger than 1 cm.
- Single large polyp with wide base
- Polyps presented with gallstones
- Polyps caused thickening wall of gallbladder
- Polyps with rapid growths
- Polyps that induce related symptoms
Gallbladder polyps should not be overlooked
Since gallbladder polyps do not exhibit any noticeable symptoms, regular health check-ups with upper abdominal ultrasound largely help to detect polyps, especially in people aged over 50. Lifestyle modifications to substantially lower risks of developing gallbladder polyps might include maintaining health weight, having regular exercise, avoiding high-fat diets and consuming healthy foods especially vegetables and fruits.