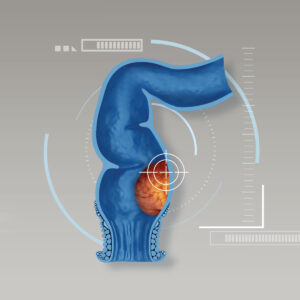
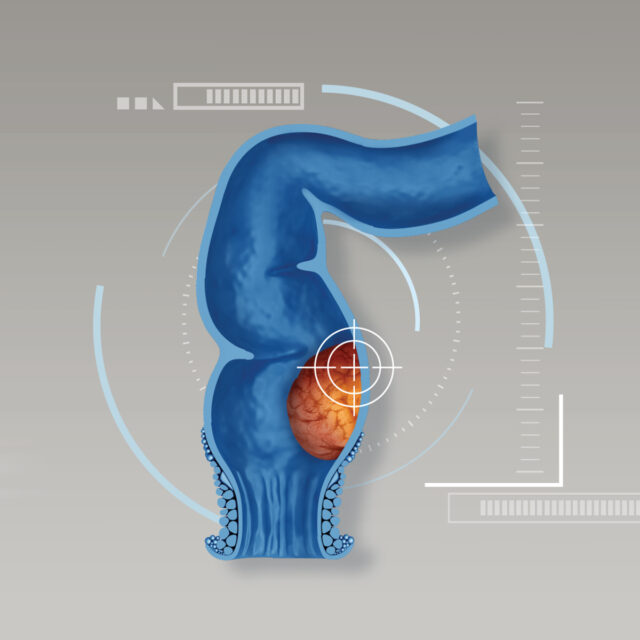
Gallstones are hardened deposits of digestive fluid mainly made of cholesterol which is formed in the gallbladder. Gallstones range in size from a grain of sand to a golf ball. It may cause no signs or symptoms. Mild to moderate symptoms that frequently disturb daily life start from abdominal discomfort to flatulence and pain after consuming high-fat diet. If gallstones lodge in a bile duct and cause a blockage, it eventually results in bile duct inflammation and infection, pancreatitis or cholecystitis (an inflammation of gallbladder). Aggravated symptoms include severe and sudden pain in the upper right abdomen especially when breathing in and out, back pain between shoulder blades, high fever, nausea, vomiting and jaundice. If cholecystitis remains untreated, it might lead to life-threatening sepsis. If the patient is an appropriate candidate for surgery, surgical removal of gallbladder is mostly advised to all cases in order to reduce disease severity and recurrence of stones which is very common. Minimally invasive surgery “laparoscopic cholecystectomy” is currently considered as an effective surgery to remove gallbladder. Due to smaller incisions, it results in less pain, fewer post-operative complications, faster recovery time and shorter hospital stay. Patients can return to daily life and activities even quicker.
Confidence in all steps of procedure
Laparoscopic surgery (laparoscopic cholecystectomy or LC) is a minimally invasive surgery to remove gallbladder which is performed by highly experienced and well-trained surgical team. The procedure involves these steps:
- Small incisions (each one inch or less in length) are made in the abdominal and umbilical areas instead of making an open large cut in the abdomen.
- The surgical instruments are inserted via these small incisions such as a laparoscope, a narrow tube with a camera. This allows surgeons to clearly visualize all dimensions of gallbladder on a screen before having it removed accurately and safely.
- Gallbladder will be then removed safely from the liver.
- After procedure is completely done, the surgical incisions will be properly closed and sealed.
Superior benefits of laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Operative areas in the abdomen can be clearly visualized through a surgical camera with high-resolution images.
- Small incisions with cosmetic benefits.
- Less pain.
- Fewer rates of post-operative infections.
- Faster recovery time.
Successful clinical outcomes of laparoscopic cholecystectomy
☑ 100% Performed by highly skilled surgical and multidisciplinary team.
☑ 100% Patient’s ability to walk within 4-6 hours after operation * in healthy candidates for surgery.
☑ 93% Success rate of operation incluing in acute cholecystitis
☑ 0 % Major injury of bile duct.
☑ 0 % Post-operative infections *in patients without cholecystitis.
Reference: Statistical data obtained from Surgery Center, Bangkok Hospital 2018.
After gallbladder removal surgery, patients do not have to be concerned about their digestive functions since gallbladder only holds bile acid and it is not essential to healthy digestion. However, to enhance the digestive health and avoid abdominal bloating, the consumption of high fat diets must be controlled with the proper amount of vegetables, fruits and easy-to-digest foods such as fish. More importantly, to achieve the best possible treatment outcomes, laparoscopic cholecystectomy should be performed by experienced and skilled surgeons which are well supported my multidisciplinary approach.