NON – INVASIVE PRENATAL TESTING (NIPT)
Screen for genetic disorders to best guide your fetus’s health.
Get to know NIPT
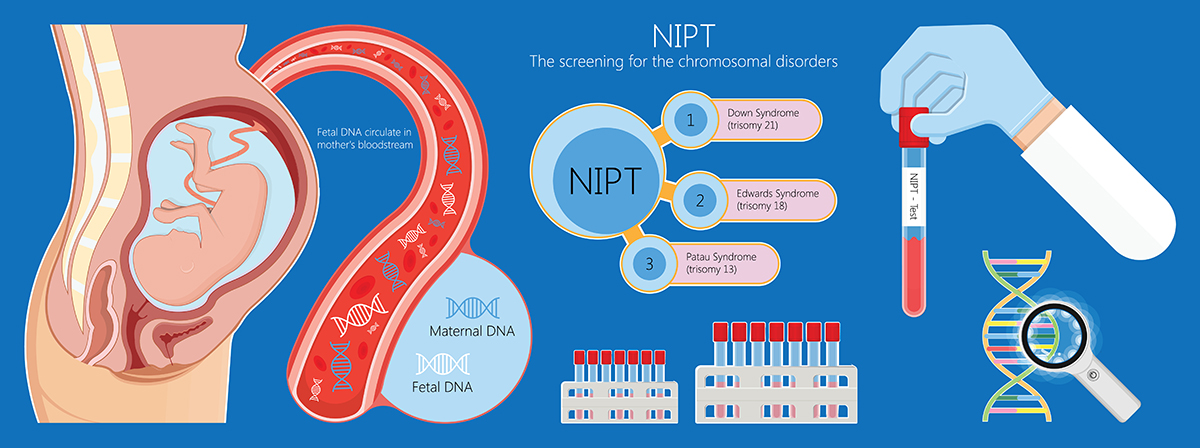
NIPT or Non – Invasive Prenatal Testing is a non-invasive screening test used to screen for the chromosomal abnormalities of the fetus using maternal blood. Besides sex chromosome of the fetus, NIPT can detect fetal risks of developing a wide range of genetic diseases caused by chromosomal anomalies, e.g. trisomy 21 Down’s syndrome, trisomy 13 and trisomy 18. NIPT is recommended when the gestation age is 11 weeks or more.
The importance of Non – Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT)
By assessing the risk of chromosomal disorders in a fetus, NIPT is highly recommended in couples who need to know the risk of having babies carrying certain inherited diseases caused by genetic abnormalities, particularly Down’s syndrome or trisomy 21 (presenting with an extra copy of chromosome 21) which is the most common autosomal trisomy.
Benefits of Non – Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT)
NIPT can minimize the need for unnecessary amniocentesis, which is an invasive testing to diagnose chromosomal conditions by removing amniotic fluid from the uterus. In the past, amniocentesis is often suggested to pregnant women aged over 35 as they pose greater risks of giving birth to a child with Down’s syndrome (> 1:250). And the risks increase dramatically with maternal age. As a reliable and highly accurate screening test, the result obtained from NIPT leads to a proper pregnancy care and planning. If NIPT shows a “low risk” result, there is no indication for amniocentesis.
Chromosomal abnormalities detected by Non – Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT)
NIPT can detect the abnormalities of chromosome 13, 18 and 21 as well as sex chromosome. Overall, NIPT offers highly accurate results with fewer false positives than other prenatal screening approaches.
|
Trisomy |
Detection rates |
False positive rates (PR) |
|
Trisomy 21 |
Detection Rate 99.5% |
False PR 0.05% |
|
Trisomy 18 |
Detection Rate 97.7% |
False PR 0.04% |
|
Trisomy 13 |
Detection Rate 96.1% |
False PR 0.06% |
|
Sex Chromosome |
Detection Rate 90.3% |
False PR 0.23% |
***All pregnant women should be advised for having NIPT and the consideration whether NIPT is needed hinges upon each individual and expert’s opinions.
Who should get Non – Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT)
Pregnant women with gestation age from 10 weeks onwards to increase the likelihood of sufficient fetal fraction.
Results obtained from Non – Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT)
- How long does it take to get the result?
The test normally takes 5 – 7 days to obtain the result. - What do I have to do if the result is positive?
For pregnant women who receive positive results from NIPT, genetic counseling is recommended along with invasive testing, e.g. amniocentesis to confirm the diagnosis.
Commonly asked questions regarding Non – Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT)
- Does NIPT pose any risks?
As a non – invasive approach using maternal blood, NIPT holds no associated risks for the mother and the fetus.
Why should I get NIPT at Bangkok Hospital?
At Women’s Health Center, Bangkok Hospital, NIPT is offered and conducted by highly expert obstetricians – gynecologists to detect chromosomal abnormalities of the fetus, including the risk of Down’s syndrome and other chromosomal anomalies while significantly reducing the miscarriage rates. With high degree of safety and result accuracy, it enables to guide for the fetal health, allowing appropriate prenatal care throughout the pregnancy time.
Tailor Your Life.Screen for genetic disorders to best guide your fetus’s health.











