Osteoporosis is one of the most common health-related problems that largely disturbs daily life and activities of the elderly. Since osteoporosis does not usually produce any noticeable symptoms therefore patients are not well aware that osteoporosis has developed. As the result of osteoporosis, the bones become more fragile due to bone deterioration and elderly patients are at greater risk for fractures when they accidentally fall.
The danger of osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is literally defined as porous bones. It is a disease in which the density and quality of bone are reduced due to advanced age. Bones become more porous and fragile, resulting in increased risks of fracture. The loss of bone occurs silently and progressively. Often there are no symptoms until the first fracture occurs. Falls often cause fractures in the elderly due to fragile and weaken bones. Therefore elderly people are prone to have fractures with minimal injuries. Treatment might be challenging and complicated, depending on severity and sites of broken bones. More importantly, elderly patients are more likely to have greater risks to fall again. Serious falls can result in decreased functional independence and quality of life. Falls in the elderly often lead to major injuries and there can be a significant associated morbidity and mortality. Fractures caused by osteoporosis most often occur in the spine, called vertebral compression fractures. Fractures can be mild injuries such as hand or wrist fractures which are not life-threatening conditions. Nevertheless, if patients have hip fractures, up to 95% of these cases essentially require hip replacement surgery. More dangerously, within a year after falls, elderly patients might have mortality rate up to 20%, being disable 30% and walking inability 40%. Approximately 80% of cases have usually lost at least one organ function. Therefore, a year after falls is a critical period since only 20% of patients can resume to their normal life and activities. The associated complications caused by being bedridden or immobility include aggravating signs and symptoms of underlying diseases, impaired heart and lung functions and poor urination with greater risks of urinary tract infection from urinary catheterization. In case of long-term being bedridden, bedsores described as ulcers that happen on areas of the skin that are under pressure from lying in bed might develop. Long treatment in the hospitals might induce brain-related conditions such as confusion, delirium and disorientation, leading to increased chances of falls and fractures again.

Prevention of osteoporosis
Fracture from osteoporosis can be potentially preventable. To reduce risks of osteoporosis, recommendations include:
- Avoid taking long-term steroidal medications.
- Consume sufficient five food groups, especially source of calcium with appropriate amount.
- Exercise regularly and stay as active as possible.
- Avoid or limit drinking alcohol and smoking.
- Have regular bone check-ups 1-2 times a year. If osteoporosis is found, addition treatment should be prescribed such as calcium, vitamin D supplements and parathyroid hormone to stimulate new bone growth and increase bone density.
Contributing factors to falls in the elderly
Risk factors for falls in the elderly include advanced age, weakness, knee osteoarthritis, impaired vision, cognitive impairment, sensory deficits and certain medication use e.g. sleeping pills. Inappropriate home setting is an environmental factor that greatly induces falls. Ergonomic home modifications include anti-slip mats and tiles in the bathroom, proper lighting especially in the risky areas such as staircases, toilet and corners, installing grab bars with even staircases and avoiding uneven surface. Patients usually fall when they walk to the toilet during night time.

Treatment of fracture with Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis (MIPO)
Severe fractures in the elderly urgently require surgical treatment within 48 hours in order to reduce serious fracture complications such as infection and thrombosis, the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel and obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system.
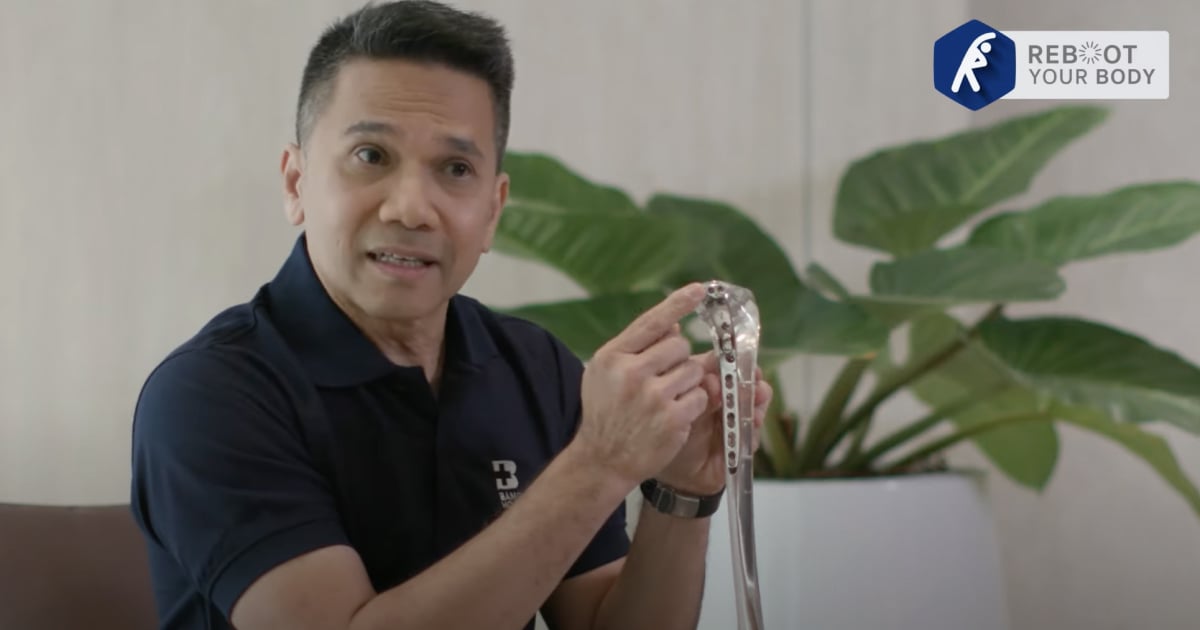
Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis (MIPO) is an emerging procedure for the treatment of fractures. This less invasive procedure is performed through small incisions, rather than having open cuts, thus fixation can be done without direct exposure of the fracture site. During the surgery, surgical instrument and a locking compression plate are inserted via small incisions to fix the affected areas. Locking compression plate will be placed above the broken bones and fixed by surgical screws. In addition, cutting-edge robotic imaging system “ARTIS pheno”, C-Arm fluoroscopic machine is used during the surgery to provide real-time 3D images of fractured areas and surrounding tissue, nerve and muscle. This advanced technology significantly improves surgical accuracy and promotes safety while minimizing time-consumption and side-effects to healthy regions.
Due to smaller incisions, it results in less pain, less blood loss and fewer pot-operative complications such as lowered infection rates. Furthermore, this surgical technique preserves soft tissue and the periosteal circulation, which promotes fracture healing, leading to faster recovery time and shorter hospital stay.
The most important things for treating patients with fractures are
- Fracture reduction and fixation to re-set and fix or repair broken bones with durable and appropriate screws, plates and other instrument.
- Surrounding areas such as healthy tissue, blood vessel and muscle must be preserved in order to promote safety and healing process.
- Implants must be properly selected in case it is needed.
- Early mobilization is crucial to avoid using orthopedic cast.