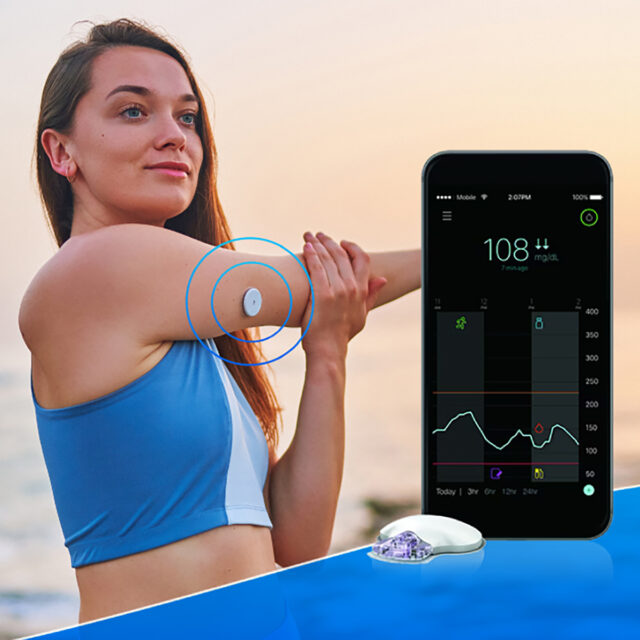
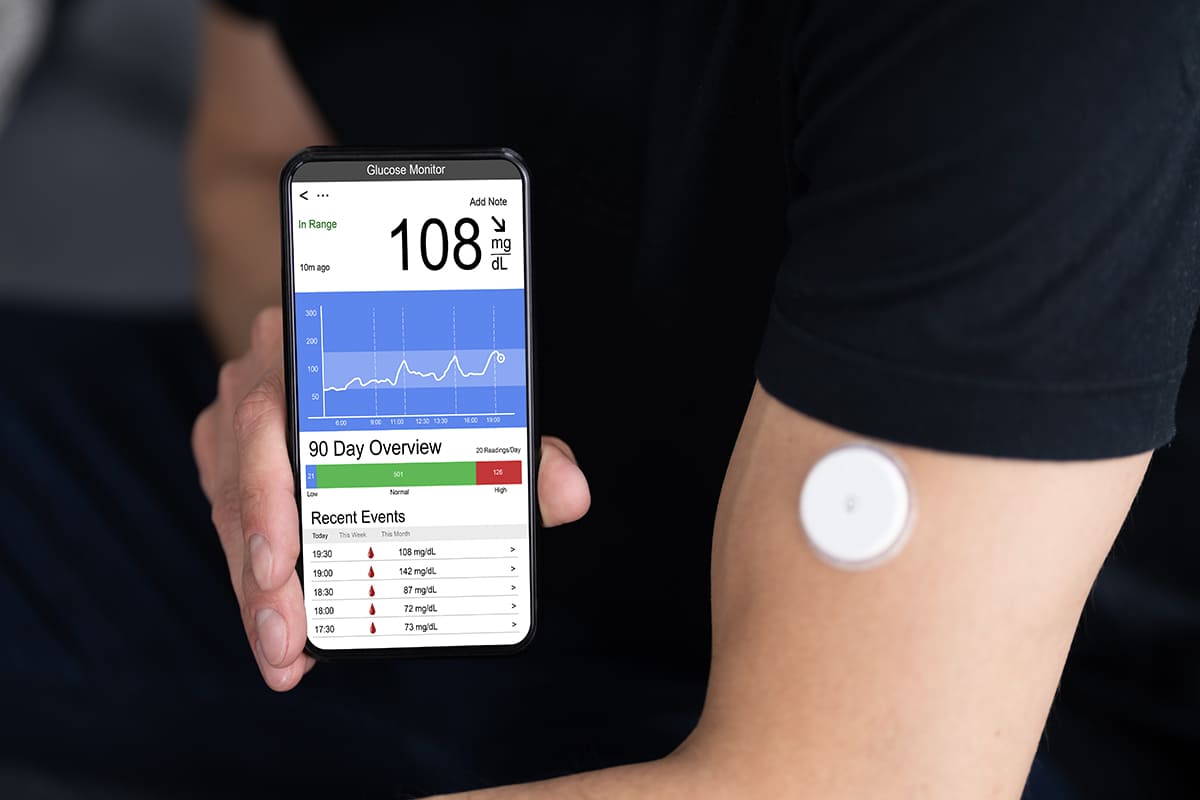
For diabetic patients, the ability to check and control blood glucose level within a safe range – not too low or too high – is essential. CGM is thus an innovative technology that has been developed to help diabetic patients keep track of blood glucose levels through smart phones in real-time, 24 hours a day continuously for 7 days, enabling their doctors to obtain complete data for diagnoses and treatment appropriately for each patient. This will also help prevent complications and severity of the disease.
What is CGM?
CGM (Continuous Glucose Monitor) is a tool for monitoring blood glucose level that can relay measurements continuously 24 hours a day for 7 days. Its sensor is attached to the patient’s arm or abdomen as prescribed by the doctor. The sensor sends data to an application on a smart phone and, in turn, to a website such that the patient can check his/her blood glucose level anytime anywhere. If the glucose is too high or too low, the monitor will send a warning about 1 hour in advance, allowing the patient time to be properly prepared. Importantly, the medical team can calibrate the monitor to match each individual patient needs in order to obtain detailed information and, thus, to help prepare a suitable treatment plan that will prevent any complication. In addition, this will provide the ability to predict possible irregular glucose value that may arise in the future. Today, glucose level reports from CGM are widely recognized and accepted. The results can also be used to guide diabetes treatments according to American Diabetes Association (ADA).
Who Should Use CGM?
- Diabetic patients.
- Obesity patients.
- People who wish to lose weight.
- Pregnant women.
- People who wish to change their eating habits and prevent diabetes.
What Are the Advantages of CGM?
- No need for finger pricking to check blood glucose level.
- Real-time blood glucose level checks every 5 minutes.
- Patients can check their blood glucose levels from mobile devices at their convenience.
- Doctors can obtain and monitor the patients’ blood glucose levels 24 hours a day.
- Convenient and easy to use, enhancing treatment effectiveness.
- Various activities are recorded to help evaluation future trends of the patients’ blood glucose levels.
- Patients can specify and modify blood glucose level notifications as desired.
What Are CGM Limitations?
CGM’s sensor has to be changed every 7 days to keep it clean as recommended by doctors, because sweats from daily activities can cause irritation on the patient’s skin. In addition, wearing a CGM may make the patient feel a little uncomfortable, though the patient can exercise and take showers normally.
What Are the Differences Between CGM and SMBG?
SMGB (Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose) is a method by which a patient can check his/her blood glucose level through finger prick tests. Though it requires a lot less blood sample than a regular test at a hospital, after frequent pricking, it can cause some discomfort that may interfere with the patient’s daily life. CGM (Continuous Glucose Monitoring), on the other hand, is a blood glucose monitoring device that only needs to have a sensor attached to the patient’s arm or abdomen. It can then report the patient’s blood glucose level 24 hours a day without finger pricking. Also, the report is internationally recognized and can readily be used in the patient’s treatment.
Why Is CGM Necessary?
When a diabetic patient’s blood glucose level is too low or too high that it can become critical, the CGM device will notify the patient as well as the patient’s medical team for prompt actions.