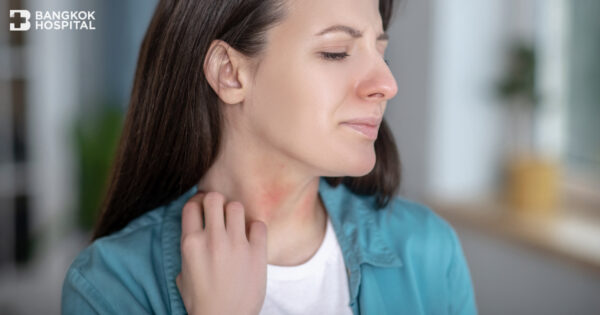
Urticaria, though not life threatening, can affect normal everyday life – especially the rashes from chronic urticaria which cause irritating itches in the long run, so much so that it can affect the quality of life including your sleep. Quick and effective treatment is, therefore, essential in improving an urticaria sufferer’s quality of life.
Getting to Know Chronic Urticaria
Chronic Urticaria exhibits rashes, or hives, that appear and reappear at least twice a week, continuously for 6 weeks or more. If the rashes remain for a length of time, it may darken the skin and some small bleeding. Moreover, urticaria can cause irritation – both physically and emotionally – which may lead to a loss of poise and self-confidence. It can also affect your ability to sleep restfully. Though it is not life-threatening, chronic urticaria could prompt other problems in the long run if left untreated
What causes Chronic Urticaria?
There are many factors that can give rise to chronic urticaria, such as:
- Food – e.g., seafood, preservatives, fermented food, etc.
- Infection – e.g., virus, bacteria, mold, etc.
- Allergic reaction to some medicines
- Some hormonal diseases, such as thyrotoxicosis – both hyper-thyroid and hypo-thyroid.
- Allergic reaction from touches – e.g., animal fur, rubber gloves, dust mites, insect stings, etc.
- Physical stimuli – e.g., heat, cold, sunlight, etc.
- Abnormal growths and cancer.
Other diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), vasculitis, etc.
Symptoms of Chronic Urticaria
The rashes caused by urticaria come in many shapes and sizes – from small to large patches. Each would show itchy, reddish raised well-defined welts on the skin without flakes. The rashes expand rapidly along the arms, legs, face, as well as around the eyes and lips. In some cases, the eyelids and lips are swollen too. Emotional stress can also affect propagation of these rashes.
Chronic Urticaria Diagnosis
- Tracing the origin of the urticaria – length of time, possible cause(s).
- Detailed medical examinations.
- Blood test.
- Other laboratory tests as prescribed by the doctor.
Chronic Urticaria Treatments
Treating chronic urticaria varies from case to case, depending on its cause and stimulating factors. The goal is to reduce the rashes with medication, such as:
- Antihistamine medicine to help control the allergic reaction. There are many different types of medication and their effects vary. As the dosage needs to be adjusted regularly over time, it is important to consult a medical specialist and you must strictly adhere to the doctor’s advice.
- In cases with severe chronic urticaria, where antihistamine medicines are not sufficient to curb the flare-up, the doctor may consider other types of medication to arrest the cause of allergy and help improve the patient’s condition as quickly as possible.
Proper Care When Suffering with Chronic Urticaria
- Avoid the cause of the allergy or its stimulant.
- Strictly follow your doctor’s advice.
- If the medication causes drowsiness which may affect work and daily life, it is important to consult your doctor for medication adjustments.
- Do not stop taking the medicine unless directly by your doctor.
- Do not scratch or peel off the affected skin.
- Ensure sufficient restful sleep, and avoid late nights.
- Avoid emotional stress.
Chronic urticaria may require a long treatment before it is under control. You should maintain a disciplined approach and take medicines as prescribed by your doctor. It is equally important to keep the regular doctor’s appointments. However, most vitally, you should sustain physical as well as emotional wellness.