Kidney Transplant Surgery
If the patient has end-stage chronic kidney disease from various conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, chronic inflammation of kidney tissue, etc., it is necessary to undergo renal replacement therapy with kidney transplant surgery to restore a good quality of life. The doctor will place a new kidney from a donor into the recipient’s abdominal cavity without removing the original kidney, which remains at the back of the abdominal cavity, unless there are indications that might lead to complications after surgery or obstruct the surgery, such as chronic infections or multiple large cysts.
Advantages of Kidney Transplant Surgery
- No need for dialysis or peritoneal dialysis
- Due to improved balance of electrolytes and fluids, dietary restrictions are reduced, allowing for increased food and water intake
- The body becomes stronger, allowing for a life close to normal, with improved quality of life
- Time for oneself and family
- Patients of childbearing age can have children normally
Limitations of Kidney Transplant Surgery
- There may be surgical risks such as bleeding, etc.
- Before and after kidney transplant surgery, immunosuppressive medication must be taken, which can lead to easy infections
- Due to the need for immunosuppressive medication, caution is required regarding food intake, such as consuming only well-cooked, clean food, avoiding raw foods, unpeeled fruits, and fresh vegetables to reduce the risk of infection
- After kidney transplant surgery, there are instances where the surgery may not be fully successful and the kidney may be rejected
Contraindications for Kidney Transplant Surgery
- Kidney disease with recoverable kidney function
- Active infections that are not yet resolved
- Untreated cancer (Active Malignancy)
- Patients using illegal substances
- Mental health patients who cannot control their symptoms
- Patients who do not cooperate with treatment or are unlikely to adhere to medication
- Patients expected to have a survival rate of less than 1 year
Assessment Before Kidney Transplant Surgery
- Assess readiness for kidney transplant surgery; health must be strong enough for surgery
- Assess certain kidney diseases that may recur after transplantation
- Assess the patient’s underlying diseases and perform cancer screenings
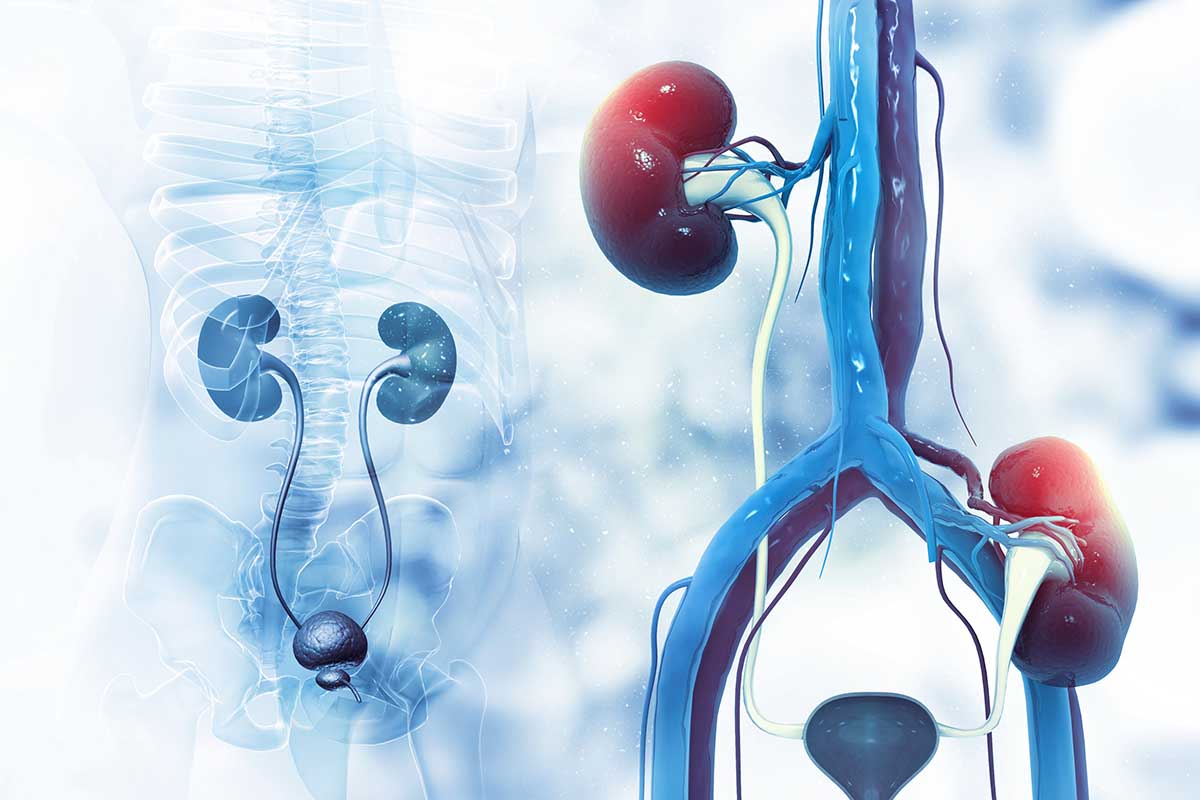
Types of Kidney Transplant Surgery
- Kidney transplantation from deceased donors (Deceased Donor Kidney Transplantation: DDKT)
The kidney to be received from the donor comes from a patient who has suffered brain death. The Red Cross selects kidneys for patients waiting for kidney donations that are the most suitable. - Kidney transplantation from living donors (Living Donor Kidney Transplantation: LDKT)
Living kidney donors (LRKT) are divided into two groups:- Living kidney donors who are biologically related to the recipient (Living Related Donor)
- Living kidney donors who are not biologically related to the recipient (Living – Unrelated Donor), such as spouses (Spouse Donor)
The advantage of kidney transplantation from living donors is that compared to kidneys from deceased donors, they have better kidney function and a longer lifespan, especially kidneys from living donors who are related due to better tissue compatibility.
Qualities of Living Kidney Donors
- Aged 20 years or older, and should not exceed 65 years, although the Thai Red Cross Organ Donation Center guidelines allow up to 70 years.
- Should not have difficult-to-control hypertension
- No heart and vascular disease
- No diabetes
- No history of chronic kidney disease
- Urine protein levels of no more than 300 mg per 24 hours
- Kidney function (GFR) greater than 80 ml/min/1.73 m²
- No dangerous obesity (BMI not exceeding 35 kg/m²)
- No serious debilitating illnesses
- Negative test for HIV (Negative test for anti-HIV)
- Willing to donate and must sign an informed consent form
- Passed psychiatric evaluation before donation
- Must be a biological relative that can be verified by laboratory test or legal means
- Must not be a case of buying or selling kidneys or receiving payment
- Relationship between donor and recipient must comply with the organ donation center’s rules
- The donor must lead a normal life after donation
Pre-Transplant Assessment for Donors
- Blood tests to assess kidney and liver function, blood concentration, and screen for hepatitis B, hepatitis C, syphilis, CMV virus, HIV, etc.
- Urinalysis to assess for protein, sugar leakage, or other abnormalities, and collection of 24-hour urine to measure waste filtration rate over 24 hours
- Chest X-ray to examine heart and lung structure and function
- Heart assessment may start with an ECG to assess heart function; if indicated, ultrasound or stress tests may occur to determine the donor’s ability to donate a kidney.
- Blood tests for tissue matching between the kidney donor and recipient
- Ultrasound by a radiology specialist to assess for abnormalities in the abdominal cavity using a probe on the abdomen
- Psychiatric assessment for mental readiness
- Consultation with an internist and surgeon performing the operation
Guidelines While Waiting for Kidney Transplant Surgery
- Submit blood tests every month to be ready for tissue compatibility testing from the kidney donor
- Attend scheduled appointments; if unable to come on the set date, call to reschedule with the staff. Missing a scheduled appointment for over a year will disqualify the patient from being on the kidney waiting list.
- If feeling unwell, see a doctor for treatment; do not self-medicate.
- If there are dental issues, treatments must be done beforehand to prevent infections, and dental check-ups should occur at least every 12 months.
- Maintain personal health and preparedness at all times, eat healthy foods, get sufficient rest, and exercise regularly; avoid places that increase the risk of infection.
- Be prepared to receive contact from the transplant coordinator nurse, as you must be ready for a kidney transplant at all times. Hence, provide a contact number that can be reached at any time, do not turn off your phone, and inform the transplant unit nurse immediately if there is a change in your phone number.
Post-Kidney Transplant Surgery Care
- Follow up for check-ups as scheduled 1 month, 3 months, 6 months, and every year with a urologist to monitor and assess health conditions regularly.
- Check with a nephrologist to assess kidney function levels, immunosuppressant levels, and evaluate complications.
- Take immunosuppressive medications as prescribed by the doctor and consistently adhere to the medication regimen.
- Ensure adequate rest and exercise regularly.
- Consume a nutritious, well-cooked, fresh, and clean diet.
- Control other underlying conditions, such as diabetes, hypertension, etc.
