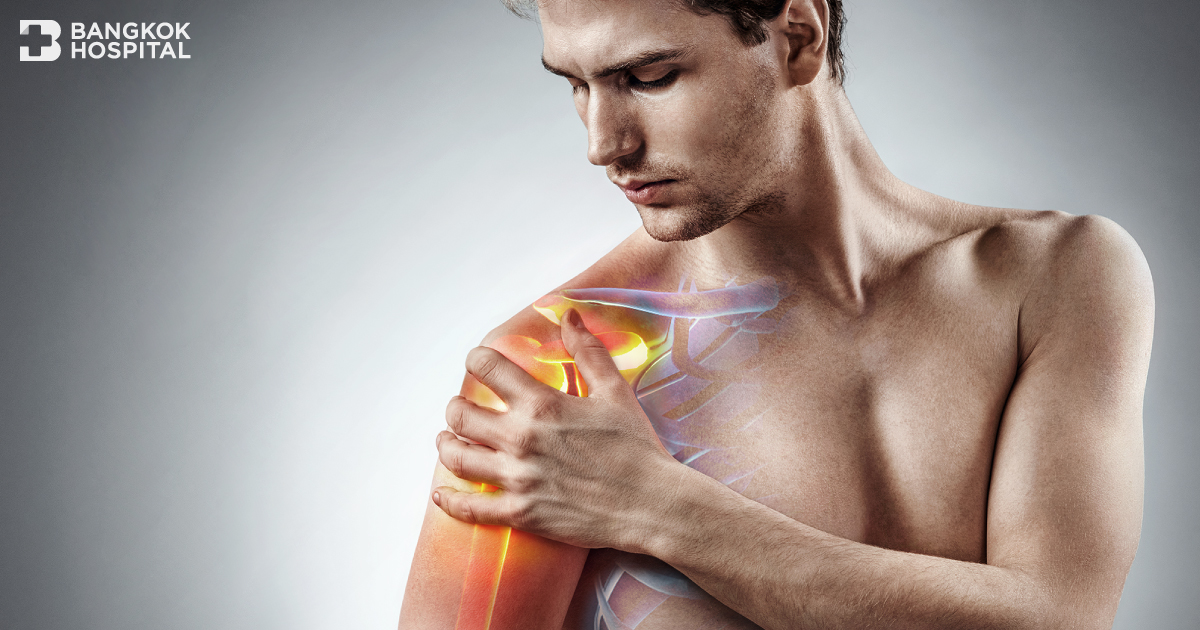
The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that surround the shoulder joint, keeping the head of your upper arm bone firmly within the shallow socket of the shoulder. A rotator cuff can be injured during activities that place a tremendous amount of force or strain on the shoulder, such as playing baseball or tennis. The severity of injury may range from a mild strain and inflammation to a partial or complete tear of one of the rotator cuff muscles that may require surgery for rotator cuff repair. In such circumstances, medical care should be provided as soon as possible.
Shoulder joint
The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint between the scapula and the humerus. It has a relatively shallow socket which results in flexibility and a range of motions. It is the most mobile joint of the human body. This ability to move makes the joint inherently unstable making the shoulder the most often dislocated joint in the body. In order to maintain a stable shoulder, there is a complex interplay between the joints, muscles and ligaments. Injury to any one of these structures can result in ongoing pain, weakness, or instability.
Common shoulder joint injuries
- Rotator cuff injury
- Tendinitis
- Bone and joint injury
Causes of shoulder joint injuries
- Heavy lifting
- Crashes
- Shoulder pulled back too hard
- Pulling an object that is too heavy
- Fall on your arm
- Fall onto the shoulder
- Overstretched shoulder
- Throwing a ball too hard
Symptoms of shoulder joint injury
- Pain deep in the shoulder
- Disturbed sleep, particularly if you lay on the affected shoulder
- Difficulty to reaching behind your back
Treatments of shoulder joint injury
Treatment options depend on the location of the injury.
- Muscle injury – rest, ice compression, anti-inflammatory and muscle relaxant medications, and physiotherapy
- Bone and joint injury or dislocation – immobilize the shoulder, placing the arm in the sling, and seek medical care right away
- Chronic injury – If the pain or injury is not getting better with medications or physiotherapy, consult a doctor to investigate the cause by MRI. MRI produces detailed pictures of the bones, tendons, muscles and blood vessels within the shoulder joint.
- Rotator cuff tear – Seek medical care immediately as surgery might be required.
Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair
Advancements in surgical techniques for rotator cuff repair includes less invasive procedures. The advantages of arthroscopic rotator cuff repair are reduced morbidities such as infection and wound complications, less blood loss, shorter recovery time, less tissue injuries, and less post-operative complications. The physiotherapy can begin as early as the first or second day after the surgery. Therefore, the recovery time is much shorter than the traditional open surgery.
Caring for your shoulders
- Warm up your arms before exercising
- Stretching before and after exercise
- Shoulder exercises to increase mobility and strength e.g. Taichi
If you experience pain in the shoulder, consult a doctor for diagnosis and begin treatment early. Arthroscopic repair can provide restoration of the patient’s normal anatomy with a relatively pain-free procedure.