Getting to Know Cesium
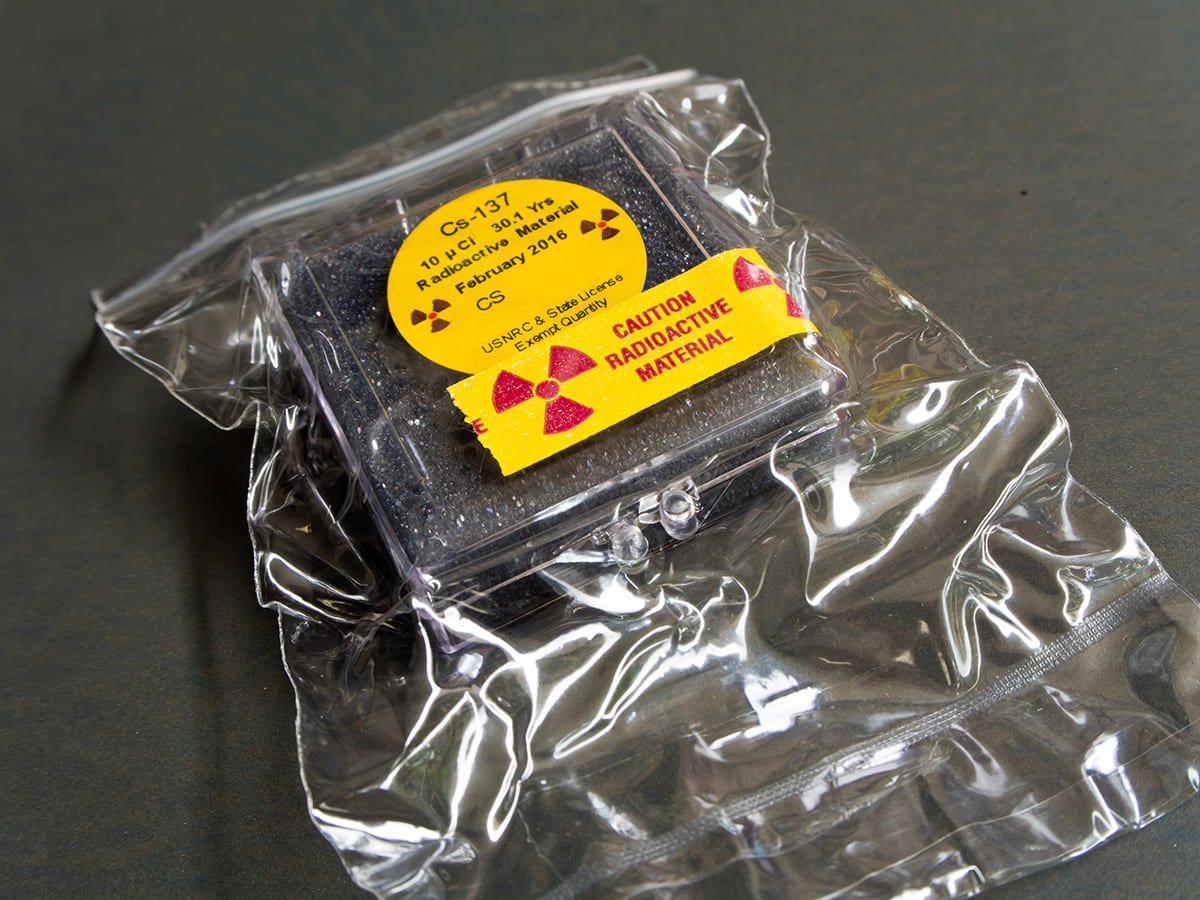
Cesium (Cesium: Cs-137) is a radioactive material, being an isotope of cesium. It appears as a solid similar to salt powder and can disperse when released from the capsules it is contained in. It has a (Half Life) of approximately 30 years. Upon decay, it releases beta radiation (Not Penetrate) about 95% and gamma radiation (Penetrate), transforming into Barium-137 (Ba-137)
Uses of Cesium
- Small amounts are used to calibrate radiation detection devices, such as Geiger-Muller counters
- Larger amounts are used for cancer treatment, measuring the flow rate of liquids in pipes, and in industry for measuring the thickness of materials such as paper, film, steel
The Severity of Cesium
The severity of radiation to the body depends on factors of exposure
- Amount of radiation
- Duration
- Part of the body
Effects of Cesium on the Body
|
Effects on the Body |
Details |
||
|
Short-Term Effects |
1) Local Radiation Injury (Cutaneous Radiation Syndrome) |
Contact with skin causing red rashes, itching, swelling, blister formation, and leads to hair or fur loss |
|
|
2) Effects on other systems in the body that occur abruptly with very high amounts (Acute Radiation Syndrome) |
Initial symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, fatigue Then, symptoms will temporarily disappear for about 1-3 weeks, followed by effects on 3 main body systems |
1) Blood system, causing bone marrow suppression, leading to lower white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets |
|
|
2) Digestive system, causing nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, and bloody stool |
|||
|
3) Nervous system, causing confusion, difficulty walking, depression, and seizures, especially in severe cases |
|||
|
Long-Term Effects |
Increases the risk of cancer, such as leukemia, thyroid cancer, etc. |
||
The Missing Cesium Incident
From the incident of the loss of cesium-137 radioactive material from a power plant in Prachinburi province
- At the site, the current radiation strength (Activity) is at 41.4 mCi, which compared with the initial radiation strength measured on March 1, 2538 is at 80 mCi, or if calculated in weight, is approximately 0.000505 grams (505 micrograms). The amount of radiation released from the steel rods containing 129 mSv/hr will result in effects on the body (2000 mGy) such as skin inflammation, rashes, swelling, redness, if hugged this rod for 15 hours and a half
- The amount of cesium radiation in the Chernobyl nuclear power plant accident (Chernobyl) on April 26, 2529 is estimated to have cesium contamination in the environment 27 kilograms (2.35×109 mCi) equivalent to more than 56.76 million times the amount of radiation in this incident (http://large.stanford.edu/courses/2012/ph241/wessells1/)
- The amount of degraded radiation in the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant accident on March 11, 2554 is estimated to have contamination of degraded cesium in the environment 17 PBq (4.60×108 mCi) equivalent to more than 11 million times the amount of radiation in this incident (https://fukushima.jaea.go.jp/QA/en/q112.#:~:text=JAEA’s%20research%20shows%20that%20the,directly%20released%20into%20the%20sea.)
The risk group from the incident of the loss of cesium-137 radioactive material 137 are those operating in the area or during the time when the steel rod suspected to contain cesium-137 radioactive material 137 is melted

Exposure to Cesium Radiation
|
Pathway of Radiation Exposure |
Details |
|
External Radiation Exposure (External Radiation Hazard) |
Through skin (Skin) |
|
Protection using the principle of (TDS Rules : Time, Distance and Shielding) ● Minimize time of exposure (Time) ● Maintain the maximum possible distance from the radiation source (Distance) ● Use shielding equipment (Shielding) |
|
|
Internal Source Radiation Exposure (Internal Radiation Hazard) |
1) Inhalation |
|
2) Consumption of contaminated items (Ingestion) |
Treatment of Acute Cesium Poisoning
Treatment of acute poisoning
- Not recommended to reduce absorption from the digestive tract (GI Decontaminate) by using Activated Charcoal
- Symptomatic treatment with fluid replacement and anti-emetic medication
- Check the electrocardiogram (EKG) because it may cause QT Prolong
- Administer antidote (Antidote), which is Prussian blue. Currently, it is not available in Thailand but is in the process of being imported for treatment. It is specifically indicated for patients with internal contamination of cesium (Internal Contamination) only and is not used for skin contact or contamination on clothing

Monitoring High-Risk Groups
Health surveillance in high-risk populations means officials or the public who have been exposed to cumulative radiation of 0.2 Gy or more in that incident, with management to monitor at least once a 1 year as follows
- History taking and physical examination
- Laboratory tests include:
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Kidney function tests (Creatinine, eGFR)
- Liver enzymes (AST, ALT)
- Urine analysis (UA)
- Blood sugar levels (FBS)
- Blood lipid levels (Lipid Profile)
- Imaging tests
- Chest X-ray
- Breast cancer screening (Mammogram and Ultrasound Breasts)
- Whole abdominal ultrasound
- Electrocardiogram (EKG)
- Other appropriate special tests
If a suspicious object is found, do not attempt to return it or prove it yourself What should be done is to cordon off the area and notify the nuclear and radiation emergency hotline 1296 Office of Atoms for Peace because radiation can only be measured using a radiation meter