Understanding Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease into the Throat
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease into the throat (LPR) is a condition that occurs when digestive fluids from the stomach flow back into the esophagus up to the throat and vocal cords.
Symptoms
Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease into the throat include- Chronic dry cough
- Frequent clearing of throat as if something is stuck in the throat
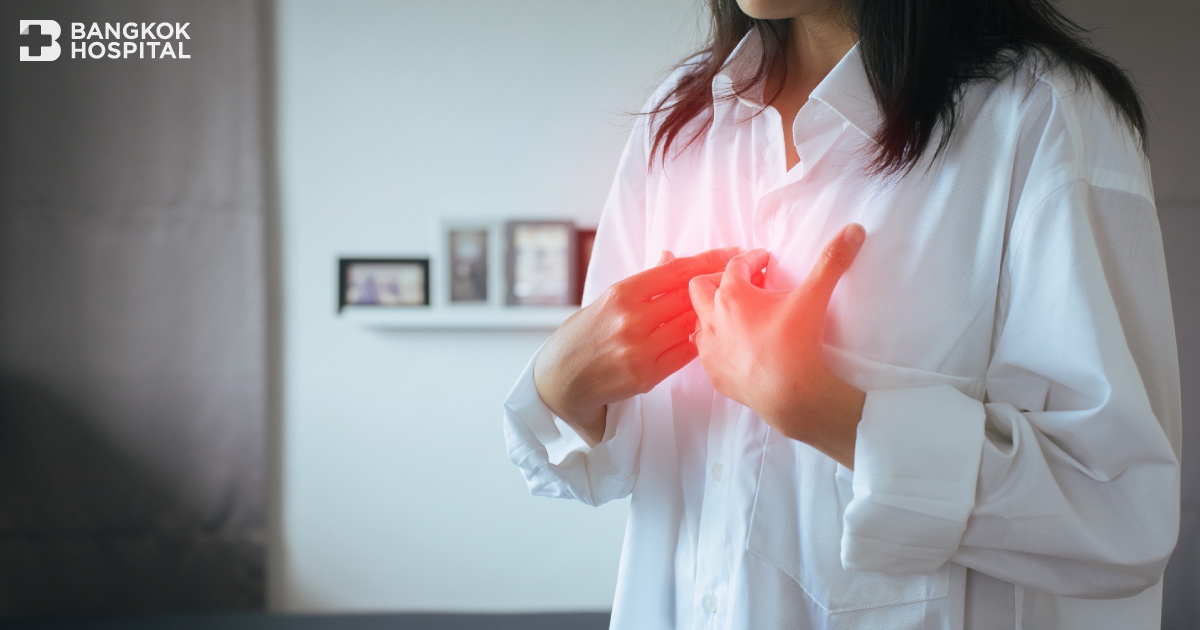
- Some cases have chest pain, while many do not. The important thing is the effect of the digestive fluids on the vocal cords and the organs in the throat area, causing various symptoms
- Some cases have hoarseness
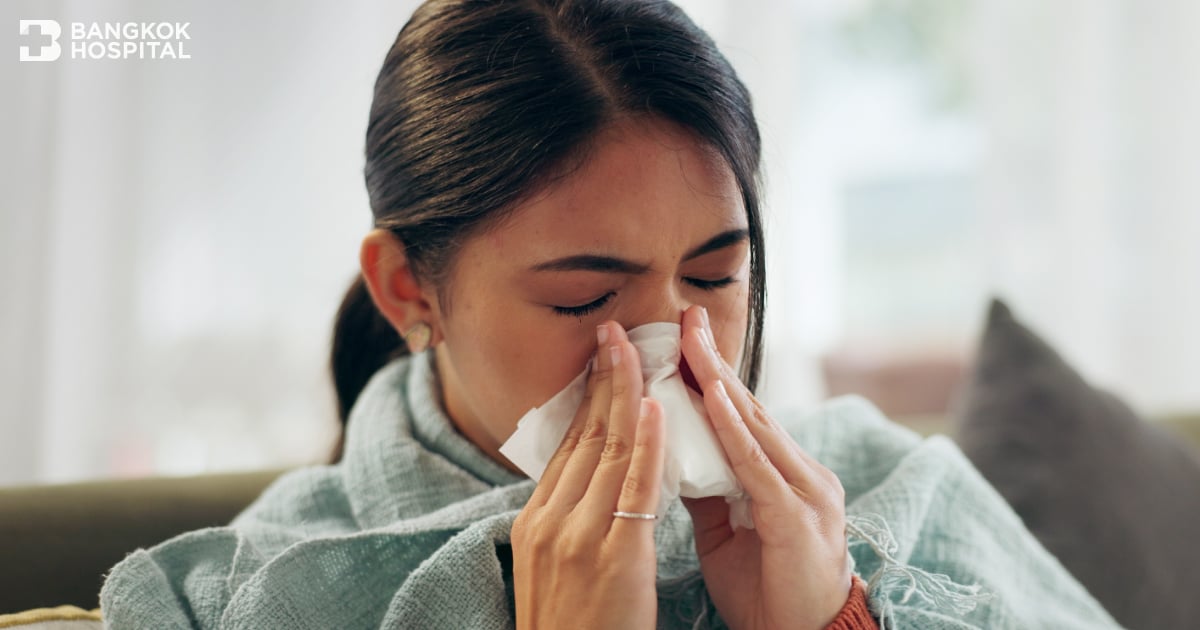
- An important but less common symptom is a runny nose. Patients often report abnormal runny nose or feeling like they have a cold
Diagnosis
- After obtaining the patient’s history, specialists will examine the head and throat, especially the inside of the throat, nose, and vocal cords, using equipment similar to a camera (Flexible Fiberoptic Laryngoscope) to look inside the throat area. If inflammation or redness is found, it may indicate Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease into the throat
- In cases where symptoms are severe and medication is ineffective, the doctor might use an Ambulatory 24-hour pH Monitoring test to analyze the cause of the disease
Treatment Methods
Treatment methods for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease into the throat are as follows
-
Changing posture and losing weight
-
Controlling and altering diet
-
Using antacids, digestive fluids reducers, or medication to aid the function of the muscles in the digestive tract
-
Surgery to prevent reflux from the stomach
-
Using medication similar to the treatment for GERD, including surgery where necessary
Duration of Treatment
The duration of treatment for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease into the throat depends on individual patients. Most will see an improvement within a 2-week period. Generally, it is recommended to continue medication for about 2 months before considering reducing the dose or stopping the medication. This disease may recur.
Prevention is Better than Cure
Practices for preventing Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease into the throat include
- Avoid smoking as it is one of the causes of GERD
- Avoid wearing tight clothing around the waist
- Avoid eating large meals before going to bed and ensure to go to bed at least 3 hours after eating
- Maintain a proper body weight
- Avoid consuming the following foods: caffeinated foods, carbonated drinks, sour drinks or mint, alcohol, high-fat foods or fried foods, eggs, chocolate, etc.
- For severe symptoms, elevate the head of the bed at least 6 – 8 inches