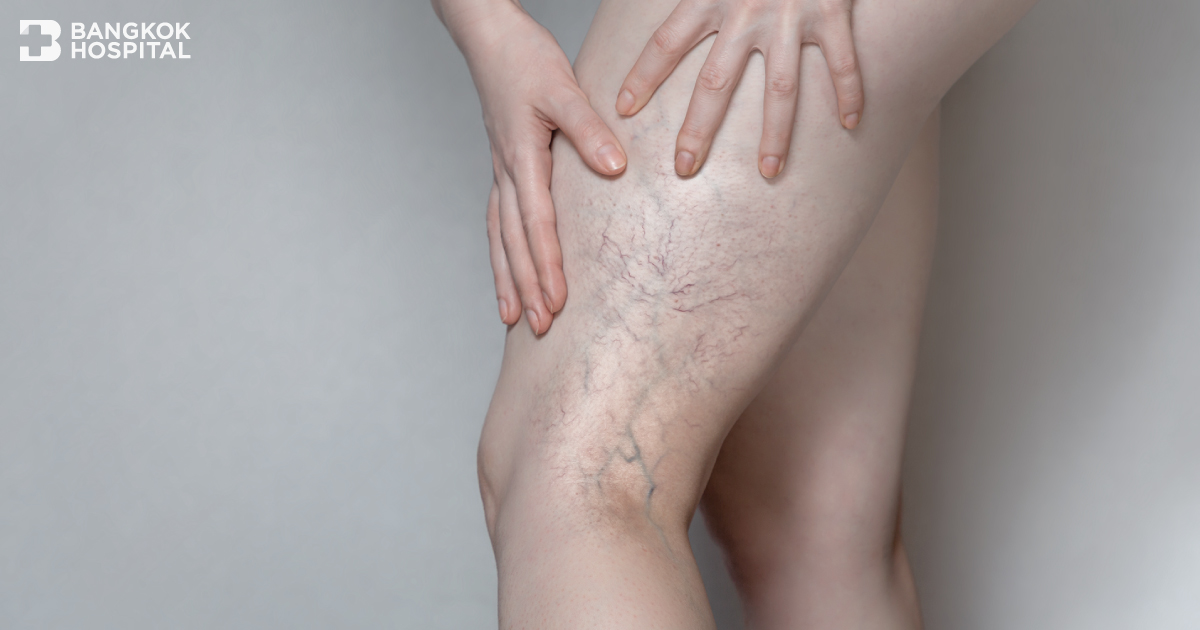
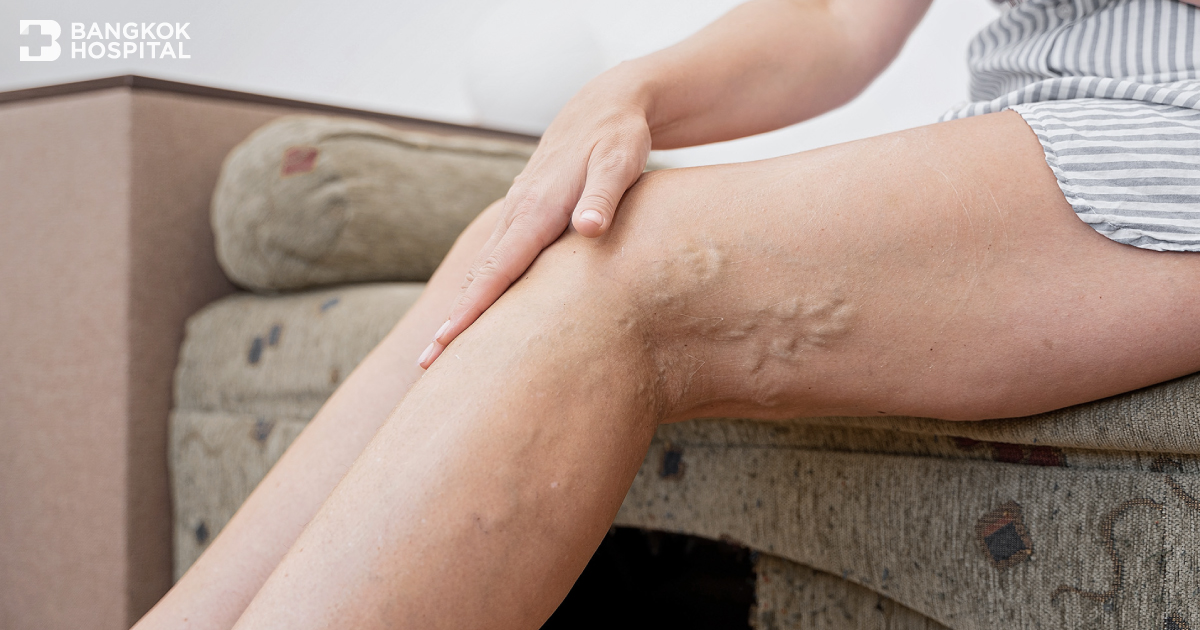
Since varicose veins might be usually perceived as a minor health problem which does not interfere daily life, these enlarged or twisted veins caused by weakened or damaged vein walls and abnormal vein valves especially in the legs are often left untreated. Without early and appropriate treatment, varicose veins potentially develop other serious complications such as chronic ulcer and bleeding. Being well aware of warning signs and knowing these 7 interesting facts about varicose veins can largely help to reduce risks and its severity.
(1) External medications such as cream do not completely cure varicose veins. To clearly diagnose, tests and procedures include medical history taking e.g. onset of symptoms, pain characteristics and other health-related conditions, physical examination, Duplex ultrasound to visualize valves in the veins whether they function normally or any evidence of a blood clot. This noninvasive technique helps identifying cause of varicose veins and the appropriate treatment could be further provided accordingly, resulting in minimized risks of disease recurrence.
(2) Varicose veins can actually occur in any part of the body. Although twisted or dilated veins can occur in any part of the body, in fact particular area commonly affected by varicose veins is the leg. Obese or overweight patients and pregnant women are at greater risks of experiencing varicose veins. Varicose veins are typically found in female rather than male. Nevertheless, male patients usually manifest more severe signs and symptoms including bulging veins that often look like big cords on the legs and inflammation of varicose veins that affect capillaries and lymphatic system in the adjacent areas.
(3) Certain occupations with prolonged sitting or standing greatly increase chances of developing varicose veins. These include lecturer or teacher, flight attendant, nurse and office worker. Owning to the veins of the legs work against gravity, prolonged period of standing leads to increase pressure in the leg compared to other parts of the body while standing up. In a combination with weakened veins and abnormal valves, the result shows up as varicose veins. In addition, during pregnancy, there are several factors that largely contribute to varicose veins including hormonal changes as well as increased weight and total body fluid that can largely affect the pressure of the veins, leading to altered blood flow.
(4) Varicose veins are likely preventable. Improving blood circulation and muscle tone can largely reduce risk of developing varicose veins or getting additional ones. Recommendations include:
• Avoiding prolonged sitting or standing.
• Changing position regularly.
• Exercising especially for improving muscle tone and vascular strength.
• Maintaining healthy weight. Controlling weight, if obese.
• Avoiding wearing tight clothes that might alter blood flow.
• Avoiding high heels and tight hosiery.
(5) Warning signs and symptoms of varicose veins include an achy or heavy feeling in the legs as well as numbness, burning, throbbing and swelling in the legs. If these abnormalities indicate, urgent medical care must be sought as soon as possible. If varicose veins are detected in early stage, chances for successful treatment substantially increase. If varicose veins are suspected, diagnostic tests typically involve Duplex ultrasound to visualize valves in the veins and additional vascular tests to determine other serious complications. Treatment is entirely determined by symptoms and disease severity.
(6) Varicose veins may exhibit different degrees of severity. Mild manifestation might only present as spider veins in the superficial skin while severe varicose veins usually appear twisted and bulging, often look like cords with skin discoloration to dark brown color and dehydrated skin which inflamed ulcer might develop.
(7) Selected treatment option is entirely determined by symptoms and presenting disease severity.
- In mild cases of varicose veins, wearing compression stockings with pressure gradient all day is often chosen as the first approach. It steadily squeezes the legs and helps veins and leg muscles circulate blood more efficiently.
- In case of small-and medium-sized varicose veins, sclerotherapy might be considered. During the procedure, small varicose veins are injected with a solution or foam that scars and closes those veins. It normally takes 15-30 minutes.
- Catheter-assisted procedures using laser energy or radiofrequency: A thin tube (catheter) is inserted into an enlarged vein. The tip of the catheter heats with either the use of radiofrequency or laser energy. As the catheter is pulled out, the heat destroys the vein by causing it to collapse and seal shut. It takes approximately 30-45 minutes in the minor operating room. Incision size is up to 0.5 cm. in length. After procedure is completed, elastic bandage will be used to wrap up the affected areas and the compression stockings will be furthered used to prevent recurrences. The degree of compression can be adjusted.
- Endoscopic vein surgery. In an advanced case involving large varicose veins, surgery might be primarily considered. With the requirements of general health assessment prior to the surgery, the operation takes 1-2 hours. Affected areas in the veins will be removed while remaining veins will be repaired. On average, incision size is 0.1-0.2 cm. For post-operative care, elastic bandage and compression stockings will be used to support the affected areas and prevent disease recurrence.
Prevention of varicose veins
To reduce risks of varicose veins, it is highly recommended to:
- Regularly exercise to enhance blood circulation in the legs.
- Change standing or sitting position.
- Elevate legs with ankle exercise while sitting by stretching and move the feet clockwise and counter clockwise to enhance blood flow to the feet and legs.
- Weight control, if obese.