1. Breastfeeding should ideally start immediately after the baby is born.
To promote mother-baby bonding which is skin-to-skin contact, breastfeeding should start immediately or within half an hour of birth. It increases the likelihood of exclusive breastfeeding with sufficient breast milk supply. As soon as breastfeeding starts, the baby spontaneously learns how to latch and the mother understands when the baby seeks for the breast milk.
2. Mother should apply appropriate breast feeding techniques.
To follow appropriate position and techniques, the mother needs to sit up right position. The baby’s head and body should be held in a straight line. The baby’s head and neck should not be twisted. The baby faces the breast with nose opposite the nipple. The mother has to hold the baby as close to the breast as possible, support the base of the baby’s head with thumb and fingers. The baby’s head slightly extends, so the nipple is aimed at the roof of the baby’s mouth and lightly touch the baby’s lip with the nipple. When the baby’s gum touches the areola that consists of milk sinuses, the baby’s tongue is placed automatically under the areola and the baby starts latching without lip compression. Sign of good attachment is the baby opens the mouth wide with lips flanged out instead of being tucked in. Pauses are noticed in between suckling. During breastfeeding, the baby swallows occasionally and it is an excellent sign for milk ingestion. When the mother is away from the baby, the mother has to preserve breast milk production. During breast milk pumping, a pump-friendly environment for breast milk secretion and collection is crucial. The mother should be able to collect breast milk at least 8 times per day with certain amount of milk. During the first 2 weeks, daily amount of breast milk should be greater than 500 ml. In addition, during the first 2 weeks, amount of breast milk in each day should be recorded in order to evaluate whether it is sufficient for the baby’s need.
3. The baby must be breastfed only
After birth, an exclusive breastfeeding is highly recommended for at least 6 months. Water, foods or other fluids are not allowed unless there are certain medical indications. Since the brain and neurological system quickly develop while the stomach remains small, a number of researches indicate that breastfeeding improves the brain development of infants. Breast milk is primarily composed of water, high amount of nutrients, vitamins, proteins, fats and immune boosting antibodies which are sufficient for a baby to grow.
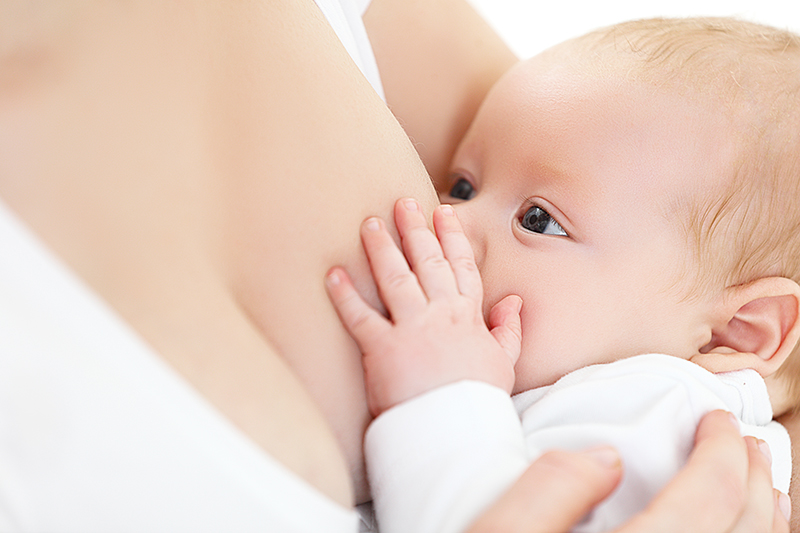

4. The mother should stay close to the baby for the first 24 hours after birth.
To encourage bonding which is the intense attachment that develops between the mother and her baby, the mother should stay close to the baby for 24 hours after childbirth. The baby will be put on the mother’s chest to promote skin-to-skin contact while the baby is an alert and wide awake phase. The baby needs to feel warm from a secure attachment bonding. Ideally, the baby will be breastfed within the first few hours after birth. Not only to preserve the mother’s nipple, but an early breastfeeding also largely helps to increase the chance of successful breastfeeding in the long run.
5. The baby can be frequently breastfed as needed.
Breast milk contains essential nutrients for the baby to grow. Frequent feeding allows the baby to practice at sucking and swallowing. While breastfeeding, the mother might hear the baby sucking and swallowing the breast milk. Moreover, frequent breastfeeding also stimulates milk production and reduces breast engorgement which happens when the breast overfills with milk. After childbirth, the mother should stay with the baby in the same room in order to keep the baby breastfed. Breastfeeding should be on demand, when the baby is hungry. An average interval of each breastfeeding should not longer than 3 hours. If the mother feels exhausted, the side-lying hold (lying down position) which the mother and baby lying down on their sides facing each other can be applied. During breast feeding in this position, the mother may take more rest and sleep.
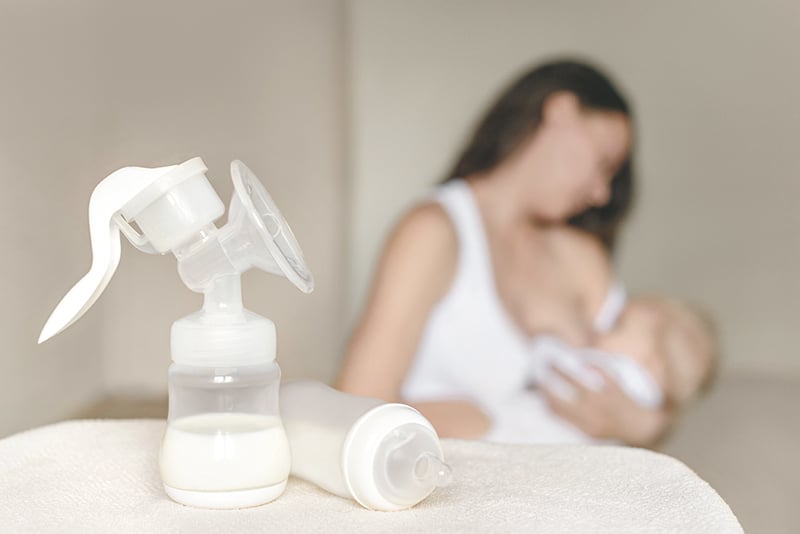

6. Nipple shields are not advised.
Getting breast milk from the nipple shields made of rubber or silicone instead of real nipple might cause nipple confusion to the baby since the sucking techniques are different. To breastfeed from the nipple, the baby needs to take the nipple far back into her/his mouth and use her/his tongue while moving jaw to pump out the milk from the milk sinuses under the areola. With nipple shields, the baby has gravity on her/his side, thus she/he can suck with the lips and get all the milk right away. This causes unfamiliarity for the baby to get back on the breastfeeding with real nipple. Eventually, the baby might develop difficulty latching on and refuse to be breastfed.
7. Breastfeeding class should be attended.
Appropriate breastfeeding techniques significantly help to increase the chance of successful breastfeeding. Antenatal care should be obtained from highly experienced health professionals in qualified hospital and prenatal class for childbirth preparation is strongly recommended. Breastfeeding Clinic aims at providing a comprehensive education and training in breastfeeding, including breastfeeding instruction, breast milk squeezing and pumping as well as breast milk storage. Holistic care of all phases during pregnancy at Breastfeeding / Lactation Clinic is provided by obstetricians-gynecologists, specialized breastfeeding nurses, pediatricians, neonatal and perinatal pediatricians (neonatal intensive care unit or NICU), nutritionists and physical therapists. The ultimate goal is to encourage the chance of breastfeeding success while solving all lactation-related problems, including breastfeeding challenges and difficulties.
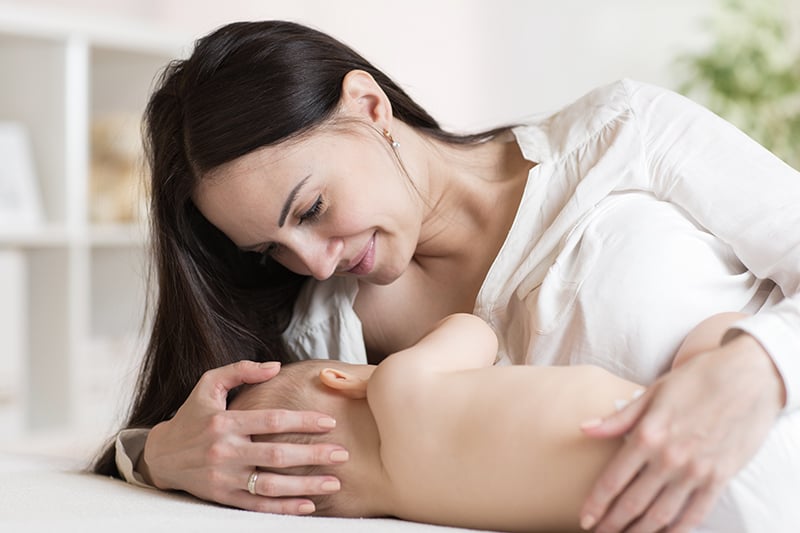

8. Mothers need to plan for pumping when returning to work
For pumping mothers who want to return to work while still breastfeeding, having a pumping plan with pump-friendly environment is vital. Some mothers stop breastfeeding when they return to work since they do not have a good environment in which to pump. WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding (the infant receives only breast milk, no other liquids or solids are given) for at least 6 months. After that, breastfeeding combined with infant supplements or formula can be continued up to 2 years or longer as the ideal feeding pattern for the infants. Mothers need to know how to correctly pump and store breast milk. During a break at work, mothers can start pumping with appropriate milk pumping equipment. More importantly, mothers need to breastfeed the babies before work in the morning and after work at night. During weekend, the babies need to be breastfed everyday. Breastfeeding substantially helps to promote more breast milk production than using breast pumps, enabling the baby to continue breastfeeding as long as possible.