Understanding Newborn Gut Obstruction
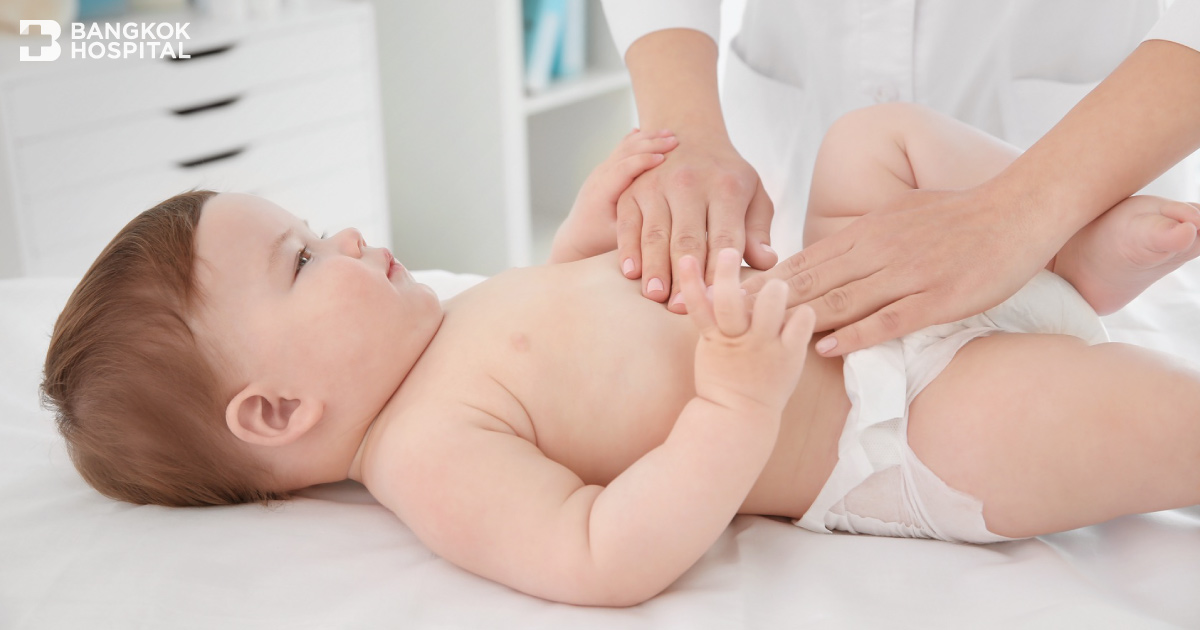
Newborn Gut Obstruction (Gut Obstruction) is a condition where the stomach or intestines are blocked, preventing food from passing through. It is considered a serious condition that can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
Recognizing the Causes
The main cause of gut obstruction in newborns stems from abnormalities in the structure of the digestive tract from the stomach to the large intestine, such as congenital pyloric stenosis, which is common between 2 – 8 weeks of age, Volvulus, Malrotation involving incorrect positioning of the digestive system, causing twisting and entanglement of the small intestine, making it impossible to pass stool to the anus. These conditions can occur at any age.
Observing the Symptoms
- Vomiting almost every time after feeding, sometimes with bile, depending on the location of the obstruction. For small intestine obstructions, symptoms include intermittent severe cramping pain around the belly button and forceful vomiting in quick succession, often including food or bile. For large intestine obstructions, vomiting is rare or mild, with a lack of flatulence, bloating, which may not be apparent initially but becomes more pronounced over time.
- In newborns, failing to pass meconium or having abnormal meconium passage, whether it is slower than normal, of lesser quantity, and paler in color.
- Not defecating or passing gas as normal, bloated stomach, which usually become noticeable around 2 – 3 days.
- Failure to thrive, poor or decreasing weight gain. If these symptoms persist for several days, the child may become dehydrated and may experience shock (sweating, cold skin, agitation, faint pulse, low blood pressure, little urine output), which can lead to dehydration, lethargy, seizures, and potentially death.
Treating Promptly
If suspected, immediately take the baby to the hospital urgently. A physical examination and special tests like x-rays will be conducted, and surgery is often required to correct the abnormality. Treatment usually involves surgery under the care of pediatric surgeons and pediatricians.