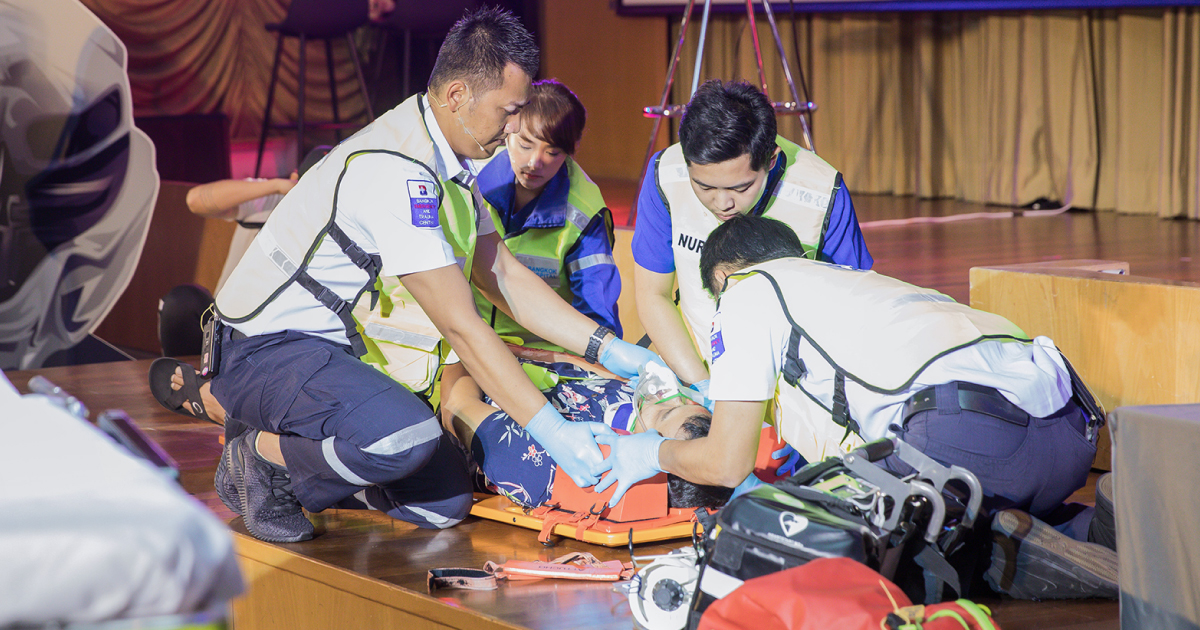
Accidents lead to injuries, deaths, or disabilities. Injured individuals should receive basic first aid and be moved to the hospital properly (Prehospital care) to ensure safety, reduce the death rate, and decrease the disability rate of the injured. Bangkok Hospital emphasizes and campaigns during the Songkran festival to boost confidence in the readiness of the medical team, nurses, multidisciplinary teams, and modern patient examination technology to handle all types of emergency accidents. It also provides proper patient care methods to increase survival chances and reduce losses during the dangerous 7 days.
Dr. Eakkarat Surakarn, Senior Director of Emergency Department and Bangkok Accident Center, Bangkok Hospital, talked about the accident statistics on the road between December 28 – January 3, 2018, or during the past New Year holiday period of the Road Accident Prevention and Reduction Center (RAPRC). It was found that there were 3,841 accidents resulting in 423 deaths and 4,005 injuries. The vehicle most involved in accidents was motorcycles, followed by pickup trucks. Speedy access to the injured and reaching the accident spot quickly is crucial, as every minute that passes for the injured is a matter of life and death. The only crucial thing that can reduce the chance of loss during such critical time is proper and timely care. Bangkok Accident Center, Bangkok Hospital, prioritizes prehospital care, an efficient patient emergency care system at the scene and during transfer to the hospital, starting from basic first aid, preliminary treatment at the scene, rapid and safe patient transfer to the hospital for ongoing treatment, including accident doctor teams, physical and mental rehabilitation, and promoting patients to be able to return to their lives. Bangkok Hospital, along with doctors, nurses, and specialized personnel trained both theoretically and practically, can make immediate and appropriate treatment decisions according to international standards, accredited by the Joint Commission International (JCI), to ensure patients or the injured have a higher chance of survival.
![]()
At the same time, regarding Scene safety or safety of the accident site, it is about assessing and creating preventive measures against danger as much as possible. For example, assessing the safety, whether the area where the accident occurred might be dangerous to the rescuers or to the public present in the incident or not. If assessed that there could be danger, rescuers should not risk helping the injured. Therefore, risk analysis should always be conducted before assisting the injured. Always remember that we are there to help the injured, not to become injured ourselves. Situation analysis involves looking and observing around the accident scene, assessing the incident, the number of vehicles involved in the accident, or the injured. The rescue team should not enter into situations involving physical or self-harm until the police declare it safe. Rapid environmental assessment prevents repeated dangers if the scene is likely to have repeated dangers, such as being hit by another vehicle, rescuers should use traffic cones or emergency lights to warn of the upcoming danger to rescuers, placing them at a suitable distance calculated according to the speed limit sign numbers. For example, if an accident occurs on a road with a speed limit of 50 km/h, the equipment should be placed 150 meters before the accident site, which will warn the vehicles to stop in time, and if it is a curve, place the cones before and at the end of the curve. Therefore, rescuers must always be cautious of possible dangers in traffic accident situations because each accident does not have a fixed formula on which method will reduce damage and injuries best. Caution to prevent occurrence is best, but in case of an accident, stay calm and think of your safety first.
Dr. Watchara Phiphobmongkol, orthopedic surgeon at the Bangkok Bone and Joint Center, Bangkok Hospital, says that in the case of obvious injuries, such as fractures or dislocations, assistance is to try to prevent further injuries. Patients who have road accidents, apart from fractures, also have damage to the periosteum, blood vessels, and surrounding tissue destroyed, bones crushing each other, or bending, causing great pain and inability to move. However, many times, bystanders seeing a clear bent fracture wish well and attempt to straighten it without knowledge, possibly causing further injuries to nearby blood vessels and nerves close to the fractured part. Therefore, what should be done is to support as still as possible. If necessary to move the patient, ensure that the broken part or the movement is minimal to prevent further injuries. If the injured can answer, ask before moving if there are neck pains or pain in the back or waist area or if unsure, wait for a rescue unit, such as emergency medical teams or doctors and nurses, which will be safer. In the case of complex fractures, multiple fragments, a comprehensive care system is required. The doctor will plan the treatment; if there are indications for surgery, will fix and hold the bone with internal metal, possibly without the need for a long incision like in the past if deemed appropriate, causing less damage to surrounding tissue, bones heal over time and can be used well, with low complications, or what is known as Minimally Invasive Surgery Plate Osteosynthesis (MIPO) for internal bone fixing metal, including both types of metal that are core inserted into the bone cavity (Nail) or using metal plates and screws (Plate and Screws), possibly inserting from the outside through small incisions to fix the deep inside bone using fluoroscope during surgery to assess accuracy and precision. The detail treatment of fracture conditions will be considered by the doctor based on suitability and severity.
Dr. Yongyut Liengudom, Director of the Bangkok Bone and Joint Center, Bangkok Hospital, says that the hand is a very complex organ. The complete operation of the hand involves small bones and joints, tendons, hand nerves, blood vessels, and skin. Common hand problems caused by 1. Accidents, such as fractures, torn tendons, severed blood vessels, severed nerves, or bruised skin. The often-broken part is the hand and wrist bones because accidents are easy to occur, seen from playing sports, car accidents, or Big Bike, as well as the elderly who fall will use their hands to support the ground. 2. Problems from work, such as inflamed tendons, carpal tunnel syndrome in the wrist, or locked fingers (from overuse). Therefore, hand treatment is complex and detailed. Treatment principles are divided according to the important components of the hand, i.e., bones and joints, should make the bones strong to move as quickly as possible. If left for too long, movement will be slow, and finger joints will easily get stuck (joint adhesions). The doctor will insert a small metal to hold the hand bones together as quickly as possible. Tendons, if the tendon at the hand is torn, the principle of tendon connection is similar to the bone; it must be connected strongly to move as quickly as possible. If treatment is delayed, it will cause scar tissue or adhesions in the tendon. Given the small space in the hand, if there is a scar, the tendon will move difficultly, and the joints will adhere more easily. The tendon part that develops a scar, if thick from the scar, will not move well. Therefore, tendon connection must be good to prevent scars or adhesions. Tendon surgery in the hand is quite difficult. The surgery has progressed a lot using the method of taking a new tendon from another part of the body to replace the problematic part, such as a tendon from the leg, leaving no scar junction so there will be no scar. Hand surgery requires a complete science whether it be bones, tendons, blood vessels, doctors who perform hand surgery must be complete, comparable to being both a goldsmith (connecting small veins through a microscope) and a carpenter (connecting bones), for example. Nerves, human hands need to have sensation; if there are nerve problems, must be treated by connecting the nerves. Given the very small size of the nerves, the connection must be precise using small threads. The more the distal part of the hand, the smaller it gets, requiring a microscope called Microsurgery. Even if there are good tendons, good bones, but if the hand has no sensation, grabbing will not work. Blood vessels are the same; if severed, they must be connected, which requires experienced doctors for targeted treatment. But if everything, bone, tendon, nerves, is severed simultaneously, everything must be connected altogether. The method is to connect bones first, followed by tendons, blood vessels, and nerves accordingly. The severed organ should be put in a clean bag, tie the bag neatly, and then immerse in ice to keep cells from dying. Do not immerse the organ directly in ice because if it gets wet, cells could die and should arrive at the hospital within 6 hours. Moreover, the hand must have sensation so it must have good skin. We might observe hand skin is different from other body parts, especially the palm skin used for touch, is particularly thick, under the skin, has a relatively large nervous system to be used so hand operation must comprise everything as mentioned. Thus, the hand can work completely and efficiently.
Dr. Chainarong Kosalasup, an expert dentist in maxillofacial surgery, says that most patients receiving treatment are often those who have had accidents involving the face, such as car accidents, falls, or being assaulted, falling from heights, etc. Normally, if the fracture is treated quickly, the chance of successful and favorable outcomes is higher than if the treatment is delayed. Patients who have had facial accidents often also have brain injuries. The medical team coordinated with neurosurgeons to assess whether the brain’s condition is suitable for surgery or not. If so, treatment must be commenced as quickly as possible through facial and jaw surgery (Maxillofacial Surgery), conducted by a multidisciplinary team consisting of plastic surgeons, ophthalmologists specializing in diseases of the eyelids, tear ducts, and eye sockets (Occuloplastic), dentists specializing in maxillofacial and facial (Maxillofacial) joined in the care, especially if there are injuries related to chewing, the dental team will take care because every part of the face is important. The difficulty occurs in patients with multiple broken bones, requiring experienced and skilled medical teams ready for treatment. Previously, common problems were patients unable to bite as before or seeing double images after treatment. Nowadays, these issues have reduced. The frequent issue is that patients delay in seeking treatment in case of minor injuries and thinking it would heal by itself. When symptoms begin to show, such as seeing double images, unable to bite, breathing issues, ear pain, etc., they then seek doctors, which is quite dangerous. Another case is, if an accident occurs and the real teeth are knocked out, try to find the tooth and handle it by the body of the tooth, do not touch the tooth root, rinse with clean water to remove dirt, immediately immerse in plain cold milk, and then promptly see the doctor. For cases requiring surgery, patients may be tied to the jaw splint for about 2-4 weeks, with the doctor scheduling follow-up appointments, such as 1 week, 2 weeks, 1 month, 3 months, and 6 months. Critical parts of the face, such as vision, chewing, the doctor’s goal is to enable patients to use it as close to the original as possible, but most importantly is prevention, such as wearing a helmet (full type) for motorcycle users, and wearing seat belts, as a primary self-care to prevent possible accidents.
Monitoring is crucial, especially during the dangerous 7 days. Unexpected accidents may occur. Bangkok Accident Center, Bangkok Hospital, has a team of specialized multidisciplinary doctors with experience available at the hospital 24 hours to ensure that patients experiencing severe emergencies will receive appropriate and satisfactory treatment. Advice is offered to patients both before treatment or those who have already received treatment, by specialist doctors, for safety because every second that passes may mean life or disability for the injured. In case of an accident or need for medical consultation when an emergency occurs, the central coordination center and facilitation of injured assistance, including receiving and forwarding patients by both land and air, can report emergencies 24 hours at the phone number. 1724 BDMS Alarm Center and emergency hotline number 1669 for emergency reporting and assistance are ready to provide emergency patients with timely treatment from the Institute of Emergency Medicine (IEM).