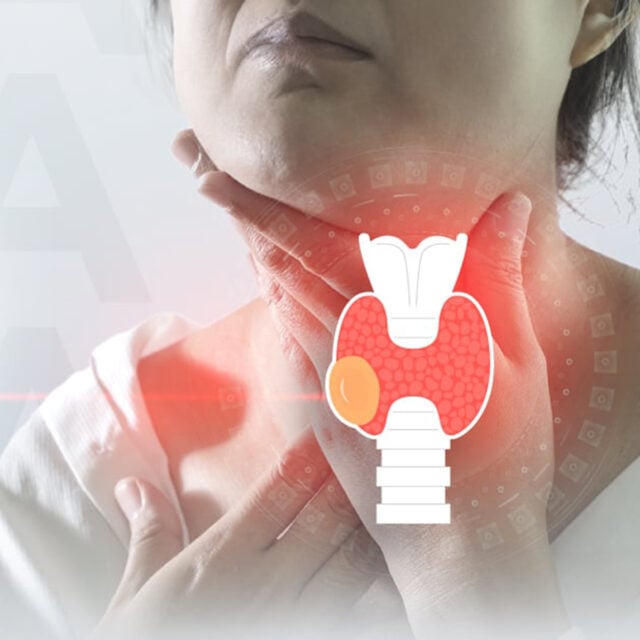
When people gain weight – experiencing swollen body or feeling uncomfortably fat – without any obvious reason, they may wonder if the conditions are due to a problem with their thyroids or a symptom of obesity. Therefore, it is essential to consult a doctor to determine the actual cause before starting any treatment, so that one will know the proper way to deal with the conditions.
THYROID AND OBESITY
Thyroid is a gland that makes and stores hormones that help regulate the rate at which food is converted into energy, body temperature, and blood pressure. If the thyroid does not work properly, other bodily functions cannot operate fully. There are many types of thyroid disease, but two of them are results of abnormal hormone production that affects the body’s metabolic system. There are:
- Hypothyroidism. This is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough of certain crucial hormones for the body’s metabolic function. As a result, the person will gain weight without an explanation, experience body swelling or dry skin, get fat effortlessly, feel tired and sleepy easily, or have increased sensitivity to cold, etc.
- Hyperthyroidism. This occurs when the thyroid gland produces too much of the hormone that regulates the body’s metabolism, causing unintentional weight loss, increased appetite but no weight gain, fatigue, more frequent bowel movements, hand tremors, irregular heartbeat, increased sensitivity to heat, etc.
There is, therefore, a correlation between thyroid gland and obesity. Hypothyroidism causes the body’s metabolism to decrease, resulting in weight gain. However, this does not always mean that a thyroid problem causes obesity, nor that an over-weight person is experiencing hypothyroidism.
Moreover, there are other diseases relating to the thyroid gland. These include tumor in thyroid, thyroiditis caused by a virus or bacteria, enlarged thyroid, and so on. So, it is crucial to observe your thyroid conditions regularly. Click https://www.bangkokhospital.com/th/bangkok/content/10-thyroid-disease-signs
CAUSES OF THYROID PROBLEMS
There are many causes of thyroid problems. These include:
- Abnormality in the body’s immune system that impairs the functions of the thyroid, making it either over- or under-active which leads to other health problems.
- After giving birth, a mother may experience postpartum thyroiditis.
- Genetic.
- Some medication may interfere with the thyroid’s function – e.g., medicines for treating irregular heartbeat or cancer.
- Iodine deficiency.
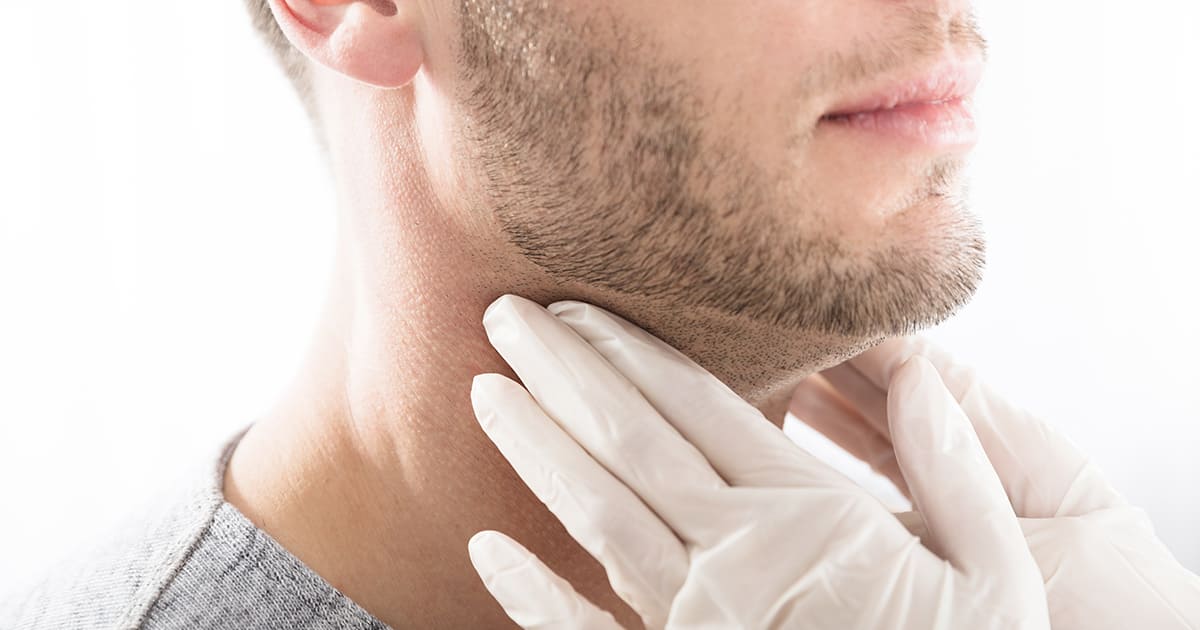
DIAGNOSIS
- Health history check.
- Medical examination.
- Physical check around the throat and neck for irregularity in the thyroid’s shape.
- Blood test to determine thyroid hormones level and thyroid antibody.
- Ultrasound scan.
- Fine needle biopsy
TREATMENT OF THYROID PROBLEMS
Treatment depends essentially on the symptoms and severity. These are:
- For the irregularity in thyroid function, medication may be prescribed to control the condition.
- If a cyst is discovered in the thyroid, aspiration or percutaneous injection may be prescribed.
- For thyroid cancer, it may be necessary to removed the thyroid through surgery.
THYROID DISEASE PREVENTION
- Eat healthy food, especially seafood with iodine content.
- Exercise regularly
- Abstain from smoking and alcoholic beverages.
- Sleep and rest sufficiently.
- Take care of stress.
If you are experiencing a thyroid problem, do not ignore it as the symptom may worsen – e.g., with irregular heartbeat, the condition may cause fatal heart failure. Therefore, you should consult a specialist and explore a course of treatment for your thyroid as soon as possible.