For many people, varicose veins characterized by spider veins are simply a cosmetic concern. Nonetheless, for some people, varicose veins can cause aching pain and discomfort and might lead to more serious problems of veins. If signs of varicose veins are indicated, medical attention provided by expert vascular doctors must be sought as soon as possible. Not only to prevent serious complications of varicose veins, but appropriate treatments largely reduce the risks of the recurrence.
Get to know “varicose veins”
Veins are blood vessels that carry blood from the body toward the heart for recirculation. In our body, systemic veins are classified into superficial veins (located in the fatty layer under the skin) and deep veins which are found in muscles or along bones. Within the veins, especially those of the legs are valves, flap like structures made of elastic tissue. The valve’s function is to keep blood moving in one direction against gravity. Muscle contractions in lower legs act as pumps and vein walls help blood returning to the heart. As a regular pattern, tiny valves in veins open as blood flows toward the heart and close to stop blood from flowing backward. If these valves are weakening or damaged, blood can flow backward and pool in the veins, causing the veins to stretch or twist, leading to varicose veins.
Severity of varicose veins
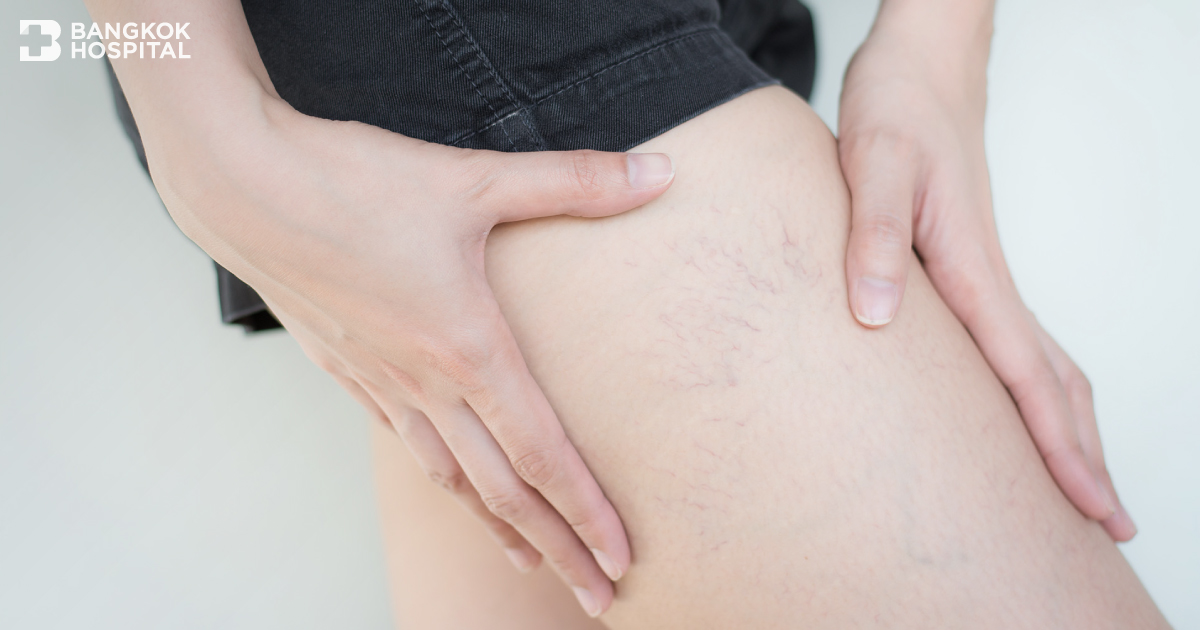
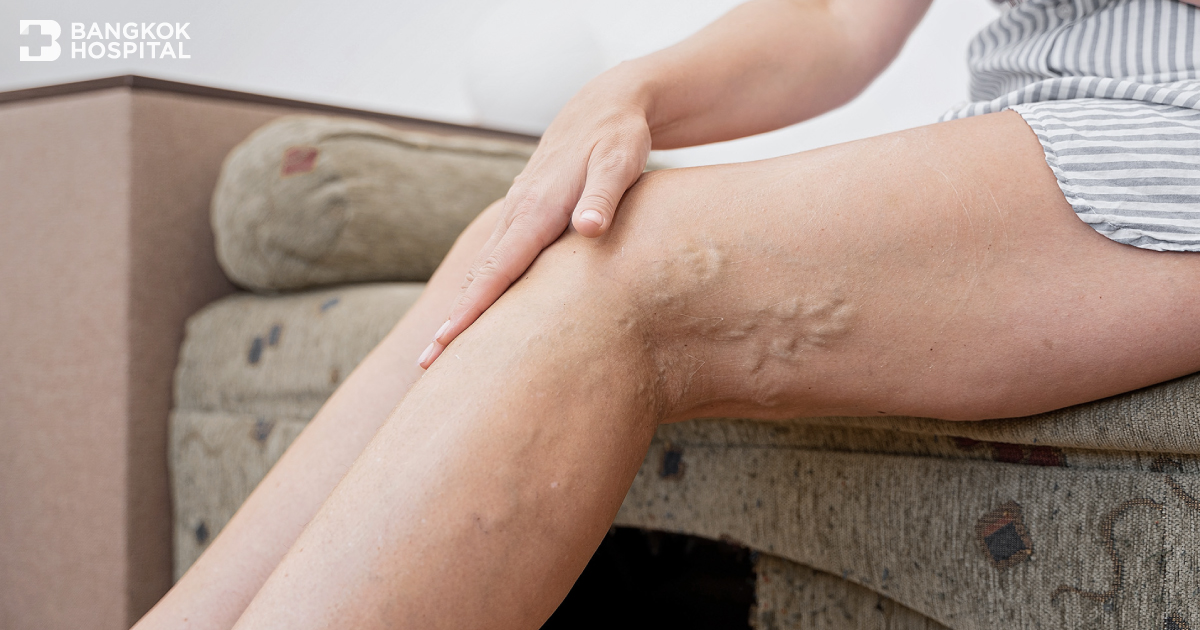
Degree of severity varies from painless spider veins, leg pain, swelling foot and leg with the presence of veins that appear twisted and bulging, often look like cords on the leg. Skin color might turn to be dark brown with rough and dry skin texture. This might lead to skin inflammation and infection.
Risk factors
- Age: Aging causes wear and tear on the valves in the veins that help regulate blood flow.
- Obesity: Being overweight puts added pressure on the veins.
- Occupation requires standing or sitting for long periods of time.
- Sex: Women are more likely to develop varicose veins. Hormonal changes during pregnancy may be a factor since female hormones tend to relax vein walls and affect valve’s function. In addition, during pregnancy, the volume of blood in the body increases, resulting in enlarged veins in the legs.
- Other factors may include abnormalities of veins and history of blood clot formation
Signs and Symptoms
Varicose veins may not cause any noticeable symptoms . Abnormalities that might indicate varicose veins include:
- Twisted and bulging veins, usually look like cords on the legs.
- Veins turn to be dark purple or blue in color.
- An achy or heavy feeling in the legs.
- Burning sensation and swelling in the lower legs.
- Worsened pain after sitting or standing for a long time.
- Bleeding from varicose veins
- Skin discoloration and infection around varicose veins. Infected wounds might be especially presented close to the ankle.
Complications
- Inflammation and obstruction of varicose veins
- Occasionally, veins very close to the skin may burst and usually cause minor bleeding.
- Painful ulcers may form on the skin near varicose veins, particularly near the ankles. If ulcers are left untreated, active major bleeding may occur.
Diagnosis
Diagnostic examination of varicose veins includes:
- Medical history including onset of symptoms, pain characteristics and other health–related conditions.
- Physical examination.
- Duplex ultrasound to visualize valves in the veins whether they function normally or any evidence of a blood clot. This noninvasive technique helps identifying cause of varicose veins and the appropriate treatment could be further provided accordingly, resulting in minimized risks of recurrence.
Treatment of varicose veins
There are several types of treatment for varicose veins. The selected option entirely depends on symptoms and its severity. Treatments include:
- Conservative treatment: In mild cases of varicose veins, wearing compression stockings with pressure gradient all day is often the first approach. It steadily squeezes the legs and helps veins and leg muscles circulate blood more efficiently. The degree of compression can be adjusted.
- Sclerotherapy: During the procedure, small-and medium-sized varicose veins are injected with a solution or foam that scars and closes those veins. Sclerotherapy doesn’t require anesthesia and hospitalization. It can be done as an out-patient procedure without requirement of food and fluid restriction prior to the procedure.
- Catheter–assisted procedures using radiofrequency or laser energy: A thin tube (catheter) will be inserted into an enlarged vein. The tip of the catheter heats with either the use of radiofrequency or laser energy. As the catheter is pulled out, the heat destroys the vein by causing it to collapse and seal shut. This procedure is the preferred treatment for larger varicose veins. Before performing this procedure, general health assessment is required as well as food and fluid restriction up to 6-8 hours before procedure begins. It takes approximately 30-45 minutes in the minor operating room. Incision size is up to 2 mm. in length. After procedure is completed, elastic bandage will be used to wrap up the affected areas and the compression stockings will be furthered used. Follow-up is needed 1-2 weeks after receiving treatment.
- Endoscopic vein surgery. In an advanced case involving leg ulcers if other techniques fail, surgery might be highly considered. With the requirements of general health assessment and food-fluid restriction 6-8 hours prior to the surgery, the operation takes 1-2 hours. For post-operative care, elastic bandage and compression stockings will be used to support the affected areas. Follow-up is needed 1-2 weeks after surgery.
Prevention of varicose veins
Risks of varicose veins can be greatly reduced by:
- Regular exercising to enhance blood circulation in the legs.
- Weight control.
- Changing sitting or standing position regularly.
- Elevating legs with ankle exercise while sitting by stretching and moving the feet clockwise and counter clockwise to enhance blood flow to the feet and legs.
Varicose veins can be effectively treated if the early diagnosis can be made in time. Do not ignore any possible signs and symptoms. Medical attention with appropriate treatments must be provided as soon as possible.